Spanning Tree Algorithm Configuration
3-93
3
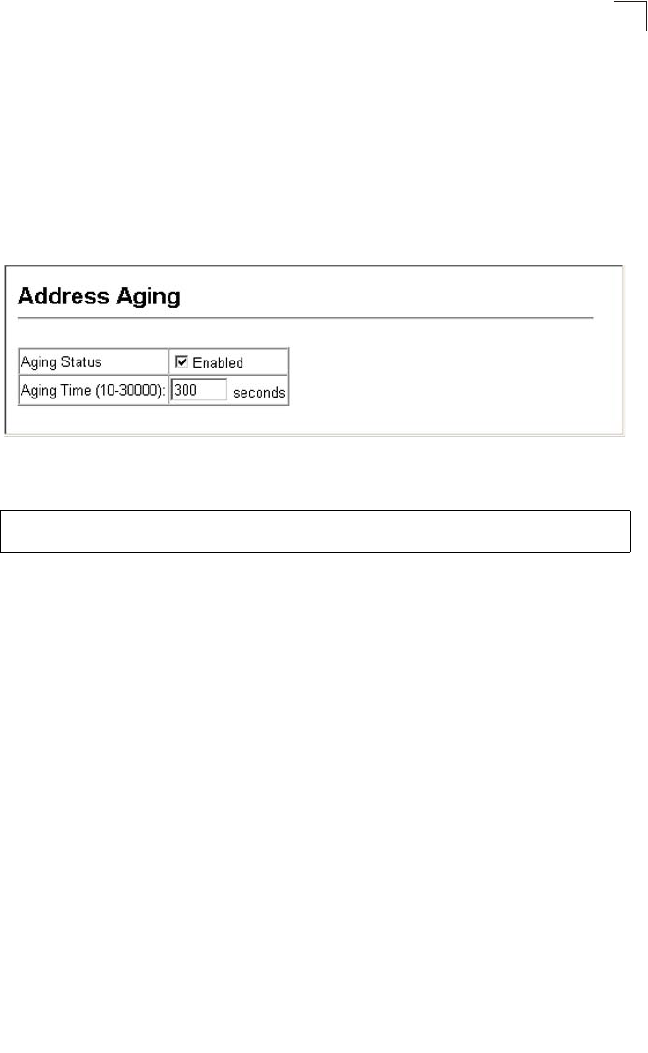
Changing the Aging Time
You can set the aging time for entries in the dynamic address table.
Command Attributes
• Aging Status – Enables/disables the function.
• Aging Time – The time after which a learned entry is discarded.
(Range: 10-30000 seconds; Default: 300 seconds)
Web – Click Address Table, Address Aging. Specify the new aging time, click Apply.
Figure 3-55 Setting the Address Aging Time
CLI – This example sets the aging time to 300 seconds.
Spanning Tree Algorithm Configuration
The Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) can be used to detect and disable network
loops, and to provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers. This allows
the switch to interact with other bridging devices (that is, an STA-compliant switch,
bridge or router) in your network to ensure that only one route exists between any
two stations on the network, and provide backup links which automatically take over
when a primary link goes down.
The spanning tree algorithms supported by this switch include these versions:
• STP – Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1D)
• RSTP – Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1w)
STA uses a distributed algorithm to select a bridging device (STA-compliant switch,
bridge or router) that serves as the root of the spanning tree network. It selects a
root port on each bridging device (except for the root device) which incurs the lowest
path cost when forwarding a packet from that device to the root device. Then it
selects a designated bridging device from each LAN which incurs the lowest path
cost when forwarding a packet from that LAN to the root device. All ports connected
to designated bridging devices are assigned as designated ports. After determining
the lowest cost spanning tree, it enables all root ports and designated ports, and
disables all other ports. Network packets are therefore only forwarded between root
ports and designated ports, eliminating any possible network loops.
Console(config)#mac-address-table aging-time 300 4-136
Console(config)#


















