Chapter 4 Theory of Operation
© National Instruments Corporation 4-9 SCXI-1503 User Manual
For temperatures above 0 °C, coefficient C equals 0, reducing this equation
to a quadratic. If you pass a known current, I
EX
, through the RTD and
measure the output voltage developed across the RTD, V
0
, you can solve
for T as follows:
where
V
0
is the measured RTD voltage.
I
EX
is the excitation current.
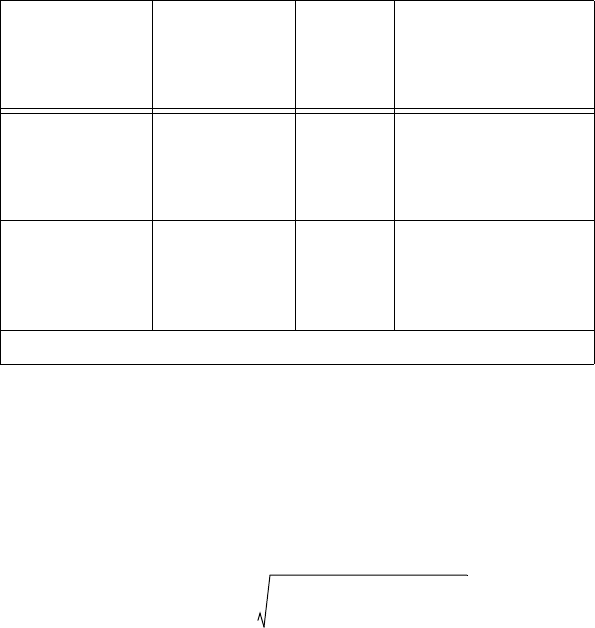
US Industrial
Standard
American
3911 100 Ω A = 3.9692 × 10
–3
B = –5.8495 × 10
–7
C = –4.233 × 10
–12
ITS-90 3928 100 Ω A = 3.9888 × 10
–3
B = –5.915 × 10
–7
C = –3.85 × 10
–12
1
No standard. Check TCR.
Table 4-1. Platinum RTD Types (Continued)
Standard
Temperature
Coefficient of
Resistance
(TCR, PPM)
Typical
R
0
Callendar-Van
Dusen Coefficient
T
R
0
V
0
I
EX
-------
–
–0.5 R
0
AR
0
2
A
2
4R
0
BR
0
V
0
I
EX
-------–
⎝⎠
⎛⎞
–+
⎝⎠
⎜⎟
⎛⎞
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------=


















