ReadyNAS 2100 User Manual
X-RAID2 and RAID C-1
v1.1, June 2009
Appendix C
X-RAID2 and RAID
This appendix introduces the main benefits of X-RAID2, and provides an overview of RAID. The
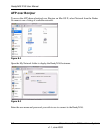
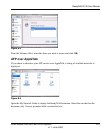
ReadyNAS 2100 supports both X-RAID2 and Flex-RAID mode. Flex-RAID mode enables a more
standard RAID configuration, whereas the proven second generation X-RAID2 mode is an auto-
expandable RAID technology that is available only on ReadyNAS and is the default configuration
on the ReadyNAS 2100.
The Benefits of X-RAID2
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, which is a way of protecting your data in
case of a disk failure. Managing RAID volumes can be a complex chore but X-RAID2 eliminates
the complexity of volume management.
X-RAID2 Is Auto-Expandable RAID
Over time, people will expand volume capacity to either add redundancy or more file storage
space. In typical RAID systems, the steps required for expanding volumes can be so complex and
error prone that it leads to data loss. X-RAID2 enables volume expansion without reformatting the
disks in the system or shuffling your data back and forth. X-RAID2 automates these complex tasks
while providing volume management features previously available only in enterprise-level storage
solutions.
Simplified Redundancy
X-RAID2 has one data volume that requires a minimum of one disk overhead to provide
redundancy and protect against disk failure. In a two-disk X-RAID2 volume, the usable capacity is
one disk, in a three-disk volume the usable capacity is two disks, in a four-disk volume, the usable
capacity is three disks, etc.
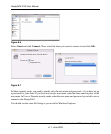
Even with RAID, there is no data redundancy with one disk; if that disk fails, your data is lost. If
you have a one-disk ReadyNAS and want protection from disk failure, you have to add a second
disk that is at least as large as the first. It can be ‘hot-added’ while the ReadyNAS is running.