ReadyNAS 2100 User Manual
Managing Your ReadyNAS 2100 2-21
v1.1, June 2009
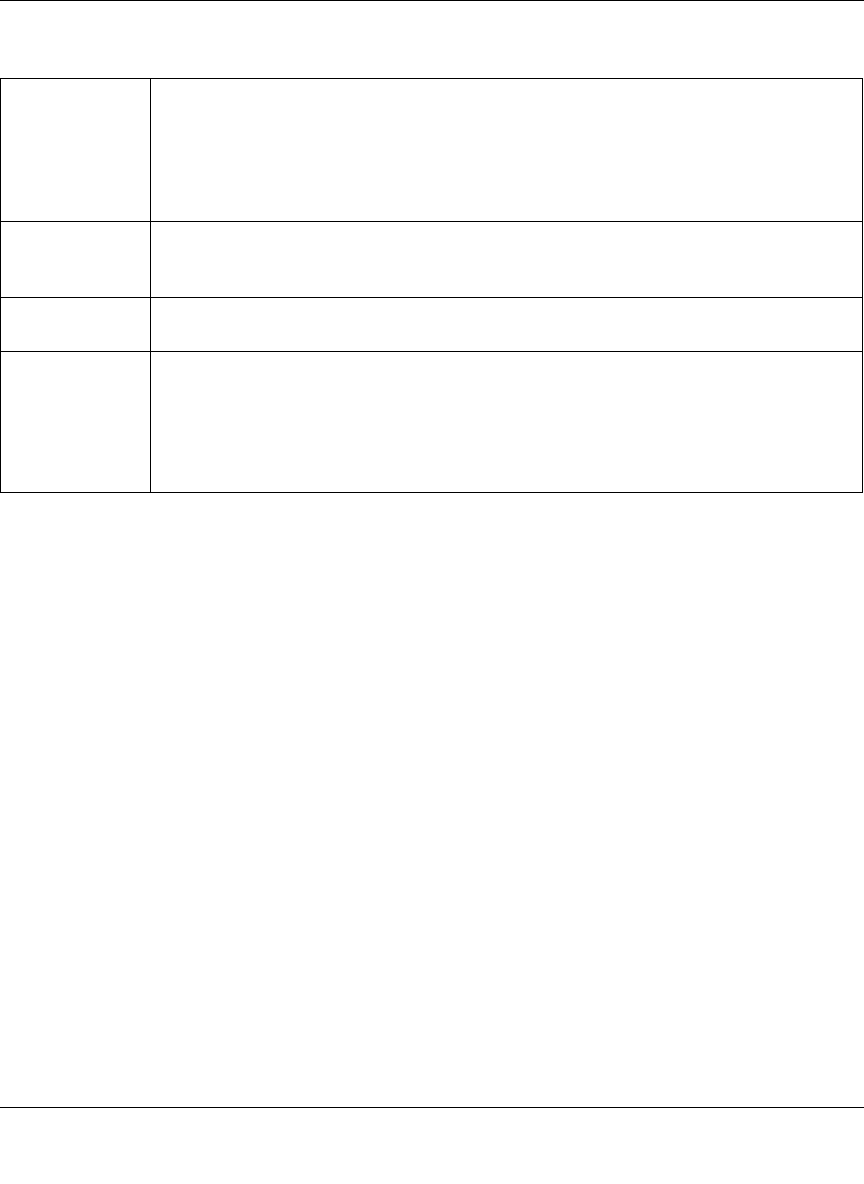
To the right of the access icons are command options. The following commands are available:
When the USB device is unmounted, you have the option of renaming it. The next time the same
device is connected, it will use the new name rather than the default USB_FLASH_n or
USB_HDD_n naming scheme.
The USB storage shares are listed in the Share screen, and access restrictions can be specified
there. The share names reflect the USB device names.
USB Flash Device Option
Toward the lower portion of the USB Storage screen is the USB Flash Device Option section (see
Figure 2-21 on page 2-20). There, you can elect to copy the content of a USB flash device
automatically on connection to a specified share. Files are copied into a unique timestamp folder to
prevent overwriting previous contents. This is useful for uploading pictures from digital cameras
and music from MP3 players without needing to power on a PC.
In User security mode, an additional option to set the ownership of the copied files is available.
Disconnect This option prepares the USB partition for disconnection by correctly unmounting the file
system. In most cases, you can safely disconnect the device without first unmounting;
however, the Disconnect command ensures that any data still in the write cache is
written out to the disks and that the file system is properly closed. The Disconnect option
unmounts all partitions on the device. Once disconnected, physically remove and re-
connect to the ReadyNAS to regain access the USB device,.
Locate In cases where you attach multiple storage devices and wish to determine which device
corresponds to the device listing, the Locate command causes the device LED to blink, if
present.
Format FAT32 This option formats the device as a FAT32 file system. FAT32 format is easily
recognizable by most newer Windows, Linux, and Unix operating systems.
Format EXT3 This option formats the device as an EXT3 file system. Select this option if you will be
accessing the USB device mainly from Linux systems or ReadyNAS devices. The
advantage of EXT3 over FAT32 is that file ownership and mode information can be
retained using this format, whereas this capability is not there with FAT32. Although not
natively present in the base operating system, Ext3 support for Windows and OS X can
be added.