Applications and features
DRAFT
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
2-5
It can also operate as a self-learning bridge supporting up to 256 MAC
addresses.
Routing
Routing is based on routing entries in a routing table. Static routes are
added via the management interface and dynamic routing is done using
RIP and RIPv2. Routing is done between the Ethernet 10Base-T
interface and the virtual channel connection (VCC) of the ATM/ADSL
interface. Optionally, the routing between the VCCs can be disabled.
M10 supports up to 8 simultaneous VCCs.
Bridging
Bridging is supported if full protocol transparency is required.
Bridging can be used simultaneously with IP routing. M10 works as a
self-learning bridge supporting up to 256 MAC addresses. Bridging is
done between the Ethernet 10Base-T interface and each ATM VCC
interface. Optionally, the bridging between the VCCs can be disabled.
M10 supports up to 8 simultaneous VCCs.
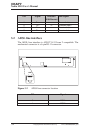
Network Address Port Translation
M10 supports Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) for TCP/IP
and UDP/IP protocols. When NAPT is used a single IP address is
allocated to a VCC to the public IP network. The Ethernet subnet has
private IP addressing and is not visible to the VCC. NAPT translates
the IP source address and source port number dynamically to the VCC
IP address and port number. Similarly packets coming from the VCC
are mapped back to the original destination addresses. NAPT allows
up to 253 hosts to share the single VCC IP address to the public
network. The Network Address Port Translation principle is presented
in Figure 2-4.
NAPT router
192.168.1.254
195.112.12.161
src:192.168.1.112:1228
dst:194.112.11.111:80
src:194.112.11.111:80
dst:192.168.1.112:1228
src:195.112.12.161:1234
dst:194.112.11.111:80
src:194.112.11.111:80
dst:195.112.12.161:1234
Home network (LAN) Internet (WAN)
Figure 2-4 Network Address Port Translation