7
Communications Services Overview Section 1-4
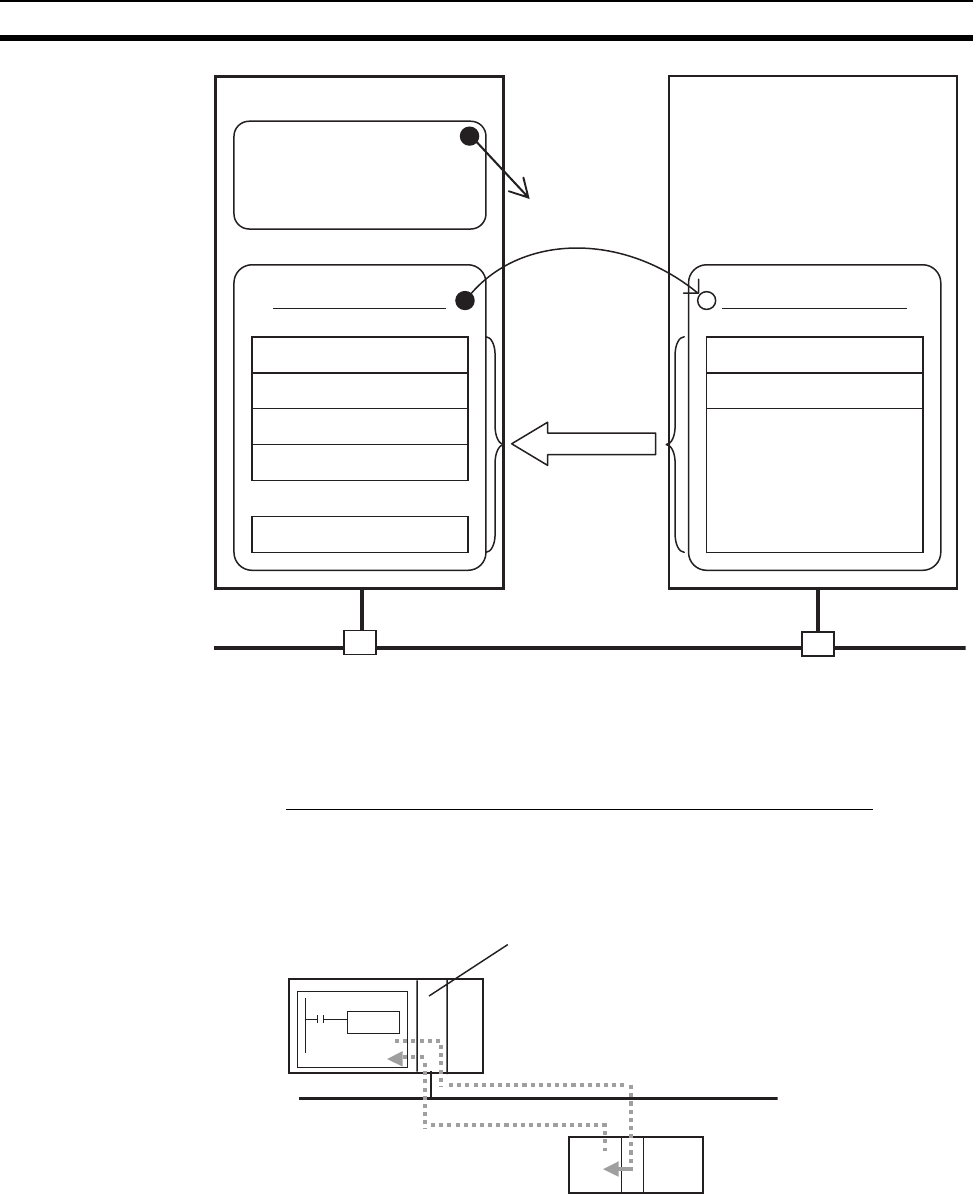
Note In this example, a connection is established with the originator’s tag list con-
taining tags a to g (inputs), which are grouped in a tag set called SP1_IN, and
the target’s tag list containing tags i and ii (outputs), which are grouped in a
tag set called SP1_OUT.
2) Message Communications (Unconnected Message Service)
User-specified CIP commands can be sent to devices on the EtherNet/IP net-
work. CIP commands, such as those for reading and writing data, can be sent
and their responses received by executing the CMND instruction from the CS/
CJ-series CPU Unit’s user program (without using a connection).
CIP messages (CIP commands and responses) can also be transferred to
another CIP-based network via the EtherNet/IP Unit or built-in EtherNet/IP
port using the CIP routing function for message communications.
In the CS/CJ Series, CIP routing is possible only through two EtherNet/IP
Units or built-in EtherNet/IP port.
Tag Set (Inputs)
Tag g
:
Tag c
Tag b
Tag a
PLC Status
EtherNet/IP
Connection information
• Target IP address
• Target tag set
• Originator tag set
• Packet interval (RPI)
Tag set name: S
P1_IN
Originator
device
Target
device
Data flow
Connection
Tag Set (Outputs)
Tag ii
Tag i
PLC Status
Tag set name: S
P1_IN
Ethernet
(EtherNet/IP)
CMND
CIP command
Response
EtherNet/IP Unit
CS/CJ-series CPU Unit