2-225
2 Instructions
CP1E CPU Unit Instructions Reference Manual(W483)
Special Math Instructions
2
APR
• Using 32-bit Signed Binary Data
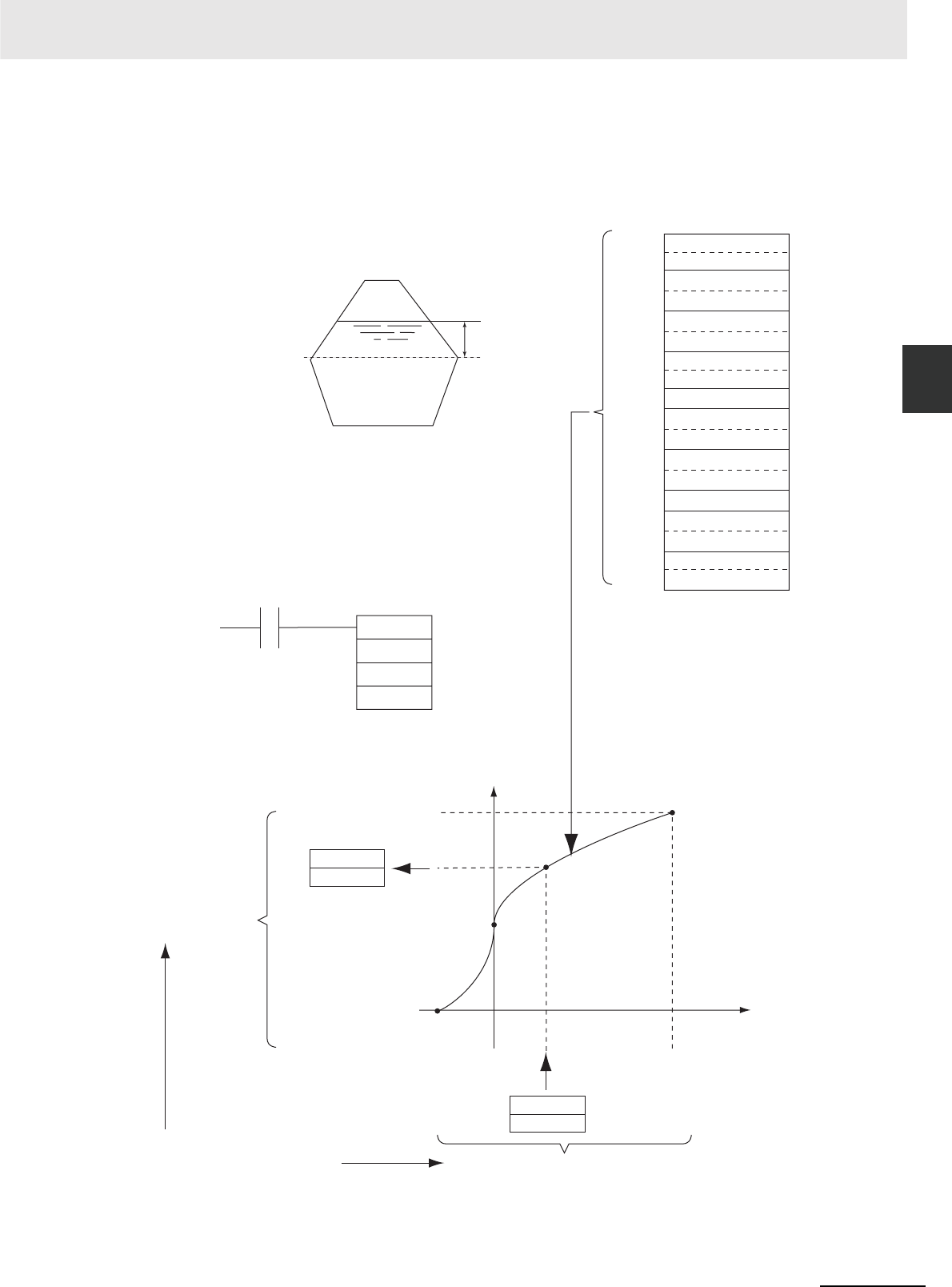
In this example, APR(069) is used to convert the fluid height in a tank to fluid volume based on the
shape of the holding tank.
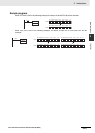
C+1
C+2
C+3
C+4
C+5
C+6
C+7
C+8
C+ (4n+1)
C+ (4n+2)
C+ (4n+3)
C+ (4n+4)
C+ (4m+1)
C+ (4m+2)
C+ (4m+3)
C+ (4m+4)
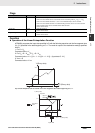
APR
C
S
R
X0
Y0
Ym
Xm
R
R+1
S
S+1
0
0.00
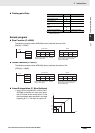
X0 (rightmost 16 bits)
X0 (leftmost 16 bits)
Y0 (rightmost 16 bits)
Y0 (leftmost 16 bits)
X1 (rightmost 16 bits)
X1 (leftmost 16 bits)
Y1 (rightmost 16 bits)
Y1 (leftmost 16 bits)
to
to
to
Xn (rightmost 16 bits)
Xn (leftmost 16 bits)
Yn (rightmost 16 bits)
Yn (leftmost 16 bits)
to
Xm (rightmost 16 bits)
Xm (leftmost 16 bits)
Ym (rightmost 16 bits)
Ym (leftmost 16 bits)
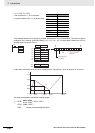
Variation from
standard = X
Fluid volume= Y
Fluid height to volume conversion table
(32-bit signed binary data)
Y data range:
−2,147,483,648 to
2,147,483,647
Y: Fluid volume
X: Variation from standard
Linear extrapolation of table
The linear extrapolation can use
signed source data if 32-bit signed
binary data is used.
High-resolution 32-bit
signed binary data
X data range: −2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647