B-1
9161-A2-GH30-30
April 1998
IP Addressing
B
Selecting an IP Addressing Scheme
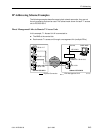
You can select from many IP addressing schemes to provide SNMP NMS, Telnet,
or FTP connectivity. When selecting a scheme, keep the following in mind:
H Because connection to remote devices is through different interfaces (for
EDL), it may be necessary to assign IP addresses and subnet masks to each
EDL individually.
H Avoid multiple EDL connections between the same two devices to prevent
routing loops.
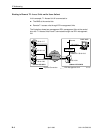
H Assign IP addresses on a per-interface or T1 access unit basis.
H Although routing information is automatically passed between interconnected
T1 access units from the network side, make sure to set a route to the
subnet(s) in the NMS’s or local router’s routing table.
The gateway to subnet(s) is through the T1 access unit connected to:
— The LAN (using a LAN adapter), or
— To a router’s, terminal server’s, or NMS’s direct PPP (point-to-point
protocol) or SLIP (link-layer protocol for IP traffic) serial connection.
H Each T1 unit’s routing table supports a maximum of 300 routes, even though
a single route is all that is needed to reach every device on a subnet.
H Have a default route set only for devices directly connected to the NMS’s
COM port.
H Allow any legal host address for a given subnet; the address choice within
the subnet is not important to the unit, but should be selected in conjunction
with all IP addressing for the subnet.
H For a point-to-point ESF T1 link, use the FDL to connect to the remote site.
H For a fractional T1 network, use EDL(s) to connect to each remote site (when
at least one data port is configured at that site).