Rev.1.02 Jul 01, 2005 page 79 of 314
REJ09B0126-0102
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NL, M16C/6NN) 11. DMAC
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
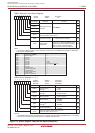
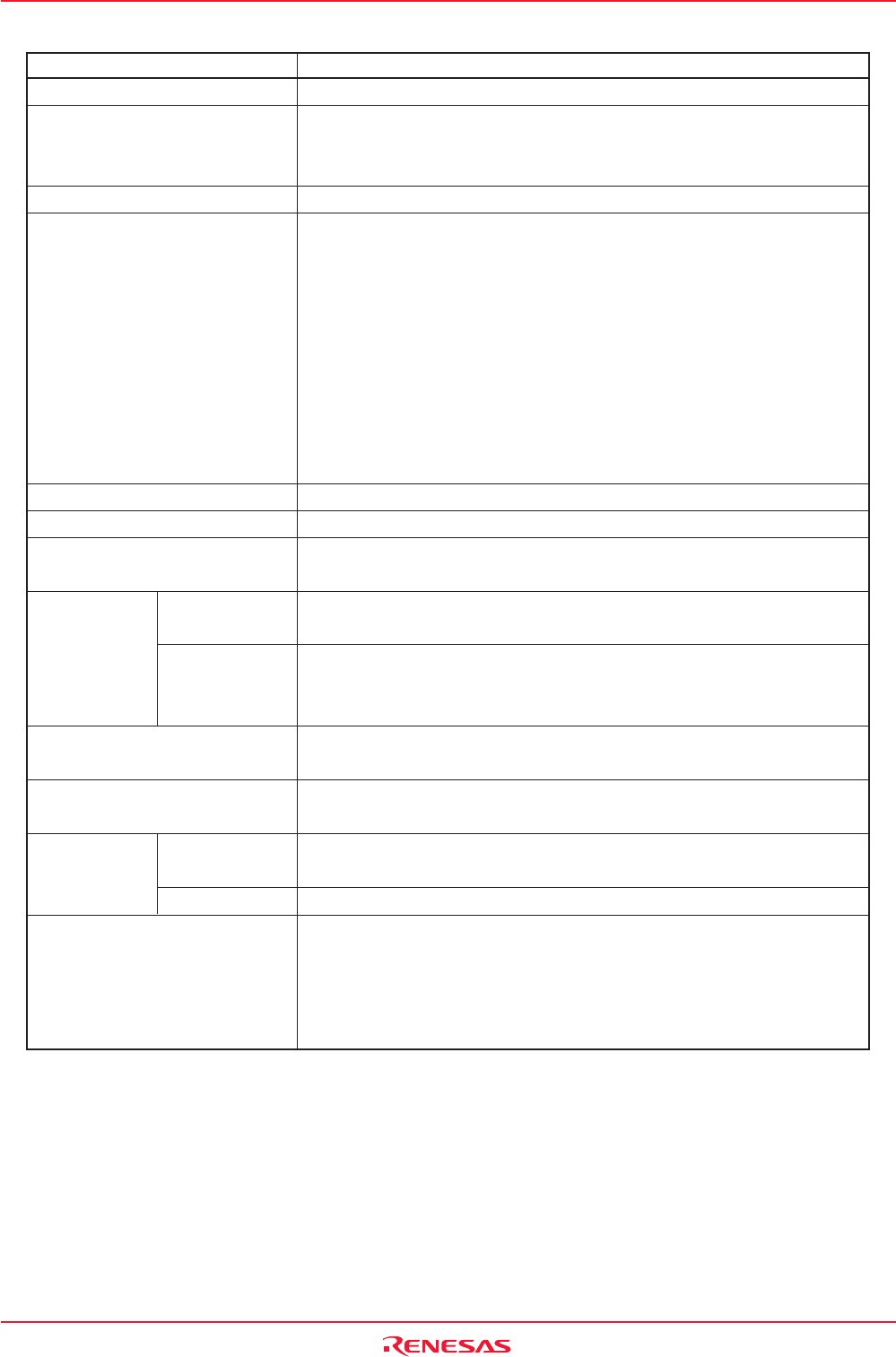
Item Specification
No. of Channels 2 (cycle steal method)
Transfer Memory Space • From any address in the 1-Mbyte space to a fixed address
• From a fixed address to any address in the 1-Mbyte space
• From a fixed address to a fixed address
Maximum No. of Bytes Transferred 128 Kbytes (with 16-bit transfer) or 64 Kbytes (with 8-bit transfer)
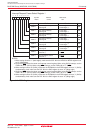
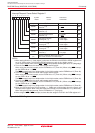
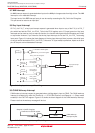
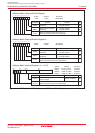
DMA Request Factors
(1) (2)
________ ________
Falling edge of INT0 or INT1
________ ________
Both edge of INT0 or INT1
Timer A0 to timer A4 interrupt requests
Timer B0 to timer B5 interrupt requests
UART0 transfer, UART0 reception interrupt requests
UART1 transfer, UART1 reception interrupt requests
UART2 transfer, UART2 reception interrupt requests
SI/O3, SI/O4 interrupt requests
A/D conversion interrupt requests
Software triggers
Channel Priority DMA0 > DMA1 (DMA0 takes precedence)
Transfer Unit 8 bits or 16 bits
Transfer Address Direction forward or fixed (The source and destination addresses cannot both be
in the forward direction.)
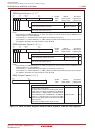
Transfer Mode Single Transfer Transfer is completed when the DMAi transfer counter underflows
after reaching the terminal count.
Repeat Transfer When the DMAi transfer counter underflows, it is reloaded with the value
of the DMAi transfer counter reload register and a DMA transfer is
continued with it.
DMA Interrupt Request When the DMAi transfer counter underflowed
Generation Timing
DMA Start Up Data transfer is initiated each time a DMA request is generated when the
The DMAE bit in the DMAiCON register = 1 (enabled).
DMA Shutdown Single Transfer • When the DMAE bit is set to “0” (disabled)
• After the DMAi transfer counter underflows
Repeat Transfer When the DMAE bit is set to “0” (disabled)
Reload Timing for Forward When a data transfer is started after setting the DMAE bit to “1” (enabled),
Address Pointer and Transfer the forward address pointer is reloaded with the value of the SARi or the
Counter DARi pointer whichever is specified to be in the forward direction and the
DMAi transfer counter is reloaded with the value of the DMAi transfer
counter reload register.
Table 11.1 DMAC Specifications
i = 0, 1
NOTES:
1. DMA transfer is not effective to any interrupt. DMA transfer is affected neither by the I flag nor by the
interrupt control register.
2. The selectable causes of DMA requests differ with each channel.
3. Make sure that no DMAC-related registers (addresses 0020h to 003Fh) are accessed by the DMAC.