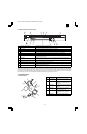
(7) Optical discharge (Semiconductor laser)
Before the drum rotation is stopped, the semiconductor laser is
radiated onto the drum to reduce the electrical resistance in the OPC
layer and eliminate residual charge, providing a uniform state to the
drum surface for the next page to be printed.
When the electrical resistance is reduced, positive charges on the
aluminum layer are moved and neutralized with negative charges on
the OPC layer.
a. Charge by the Scorotron charger
<1> Function
The Scorotron charger functions to maintain the surface potential of
the drum even at all times which. It is used to control the surface
potential regardless of the charge characteristics of the photoconduc-
tor.
<2> Basic function
A screen grid is placed between the saw tooth and the photoconduc-
tor. A stable voltage is added to the screen grid to maintain the
corona current on the photoconductor. As the photoconductor is
charged by the saw tooth from the main corona unit, the surface
potential increases. This increases the current flowing through the
screen grid. When the photoconductor potential nears the grid poten-
tial, the current turns to flow to the grid so that the photoconductor
potential can be maintained at a stable level.
b. Process controlling
<1> Function
The print pattern signal is converted into an invisible image by the
semiconductor laser using negative to positive (reversible) developing
method. Therefore, if the developing bias is added before the drum is
charged, toner is attracted onto the drum. If the developing bias is not
added when the drum is charged, the carrier is attracted to the drum
because of the strong electrostatic force of the drum.
To avoid this, the process is controlled by adjusting the drum poten-
tial and the grid potential of the Scorotron charger.
<2> Basic function
Voltage added to the screen grid can be selected, high and low.
To make it easily understood, the figure below shows voltage transi-
tion at the developer unit.
<3> Start
1) Because the grid potential is at a low level, the drum potential is at
about –400V. (Carrier may not be attracted though the carrier is
pulled towards the drum by the electrostatic force of –400V.)
2) Developing bias (–400V) is applied when the photoconductor
potential is switched from LOW to HIGH.
3) Once developing bias (–400V) is applied and the photo conductor
potential rises to HIGH, toner will not be attracted to the drum.
<4> Stop
The reverse sequence takes place.
c. Retaining developing bias at an abnormal occurrence
<1> Function
The developing bias will be lost if the power supply was removed
during print process. In this event, the drum potential slightly abates
and the carrier makes deposits on the drum because of strong static
power. To prevent this, the machine incorporates a function to retain
the developing bias for a certain period and decrease the voltage
gradually against possible power loss.
<2> Basic function
Normally, the developing bias voltage is retained for a certain time
before the drum comes to a complete stop if the machine should stop
before completing the normal print cycle. The developing bias can be
added before resuming the operation after an abnormal interruption.
Therefore, carrier will not make a deposit on the drum surface.
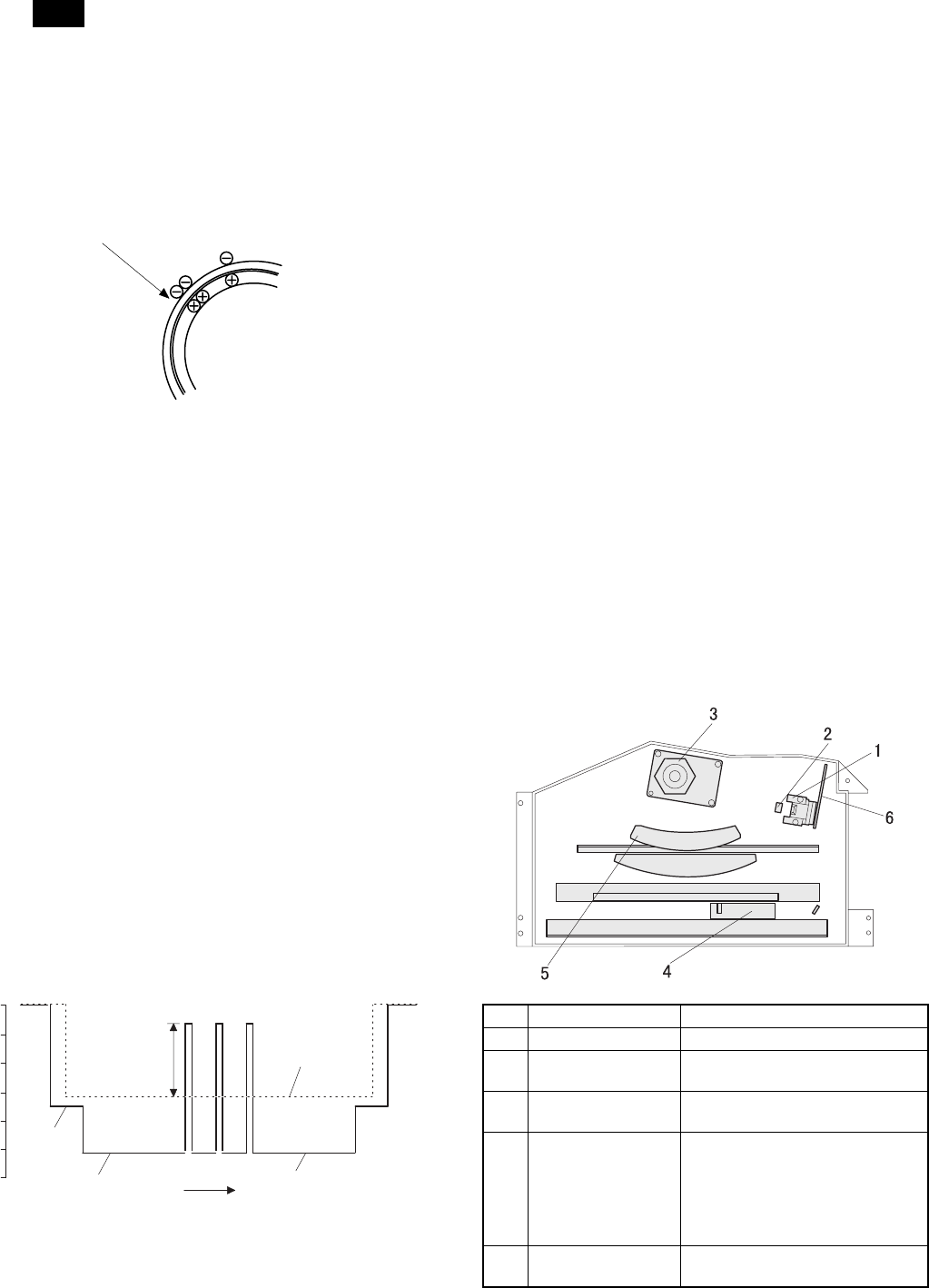
4. Laser unit
The image data sent from the MCU (image process circuit) is sent to
the LSU (laser unit), where it is converted into laser beams.
A. Basic structure
The LSU unit is the writing section of the digital optical system.
The semiconductor laser is used as the light source, and images are
formed on the OPC drum by the polygon mirror and fθ lens, etc.
The laser beams are passed through the collimator lens, the cylindri-
cal lens, the polygon mirror, the fθ lens, and the mirror to form images
on the OPC drum in the main scanning direction. The laser emitting
PWB is provided with the APC (auto power control) in order to
eliminate fluctuations in the laser power. The BD PWB works for
measurement of the laser writing start point.
1 Semiconductor laser Generates laser beams
2 Collimator lens Converges laser beams in parallel
3 Polygon
mirror,polygon motor
Reflects laser beams at a constant
rpm
4 BD (Mirror, lens,
PWB)
Detects start timing of laser
scanning
5fθ lens Converges laser beams at a spot
on the drum.
Makes the laser scanning speeds
at both ends of the drum same as
each other. (Refer to the figure
below.)
6 Laser emitting PWB Emits laser beams according to the
image data.
Semiconductor laser
0
START STOP
Print potentioal
Toner attract
potential
2)
3)
1)
Low
4)
High
Drum potential
Developing bias
Time
AR-160/161 FM/E [6] OPERATIONAL DESCRIPTIONS 11/27/1998
AR-161
6 – 5