Sending Data to Your Network Application
Rev 1.5 Jul.08 69
The problem created by Network Address
Translation
Note: A similar problem may
occur if NAT is in use on your
network. The host application
may reside on a server that has
a private IP address. You must
configure the MP modem to
send data to a server on your
network with a public IP address,
and configure the server to
recognize the MTP data and
route it appropriately.
ManyserviceprovidersuseNAT(NetworkAddressTrans‐
lation)whicheffectivelycreatesafirewallinfrontofthe
network.Insidethenetwork,theserviceprovidersassign
privateIPaddressestoregistereddevices,sincepublicIP
addressesarenotneededtoroutedatawithinthenetwork.
(Thissavestheserviceprovidertheexpenseofhavingalarge
poolofpublic
IPaddresses.)ApublicIPaddressissubstituted
fortheprivateIPaddresswhendatapacketspassthroughthe
gatewaybetweenthenetworkandtheInternet.ThispublicIP
addressmightbeusedondatatransmissionsfrommany
differentdevices.Therefore,thenetworkserverisonlyaware
ofthesubstituted
publicIPaddress.Iftheserverrepliestothis
address,thenetworkcannotidentifythedeviceforwhichthe
datawasintended.
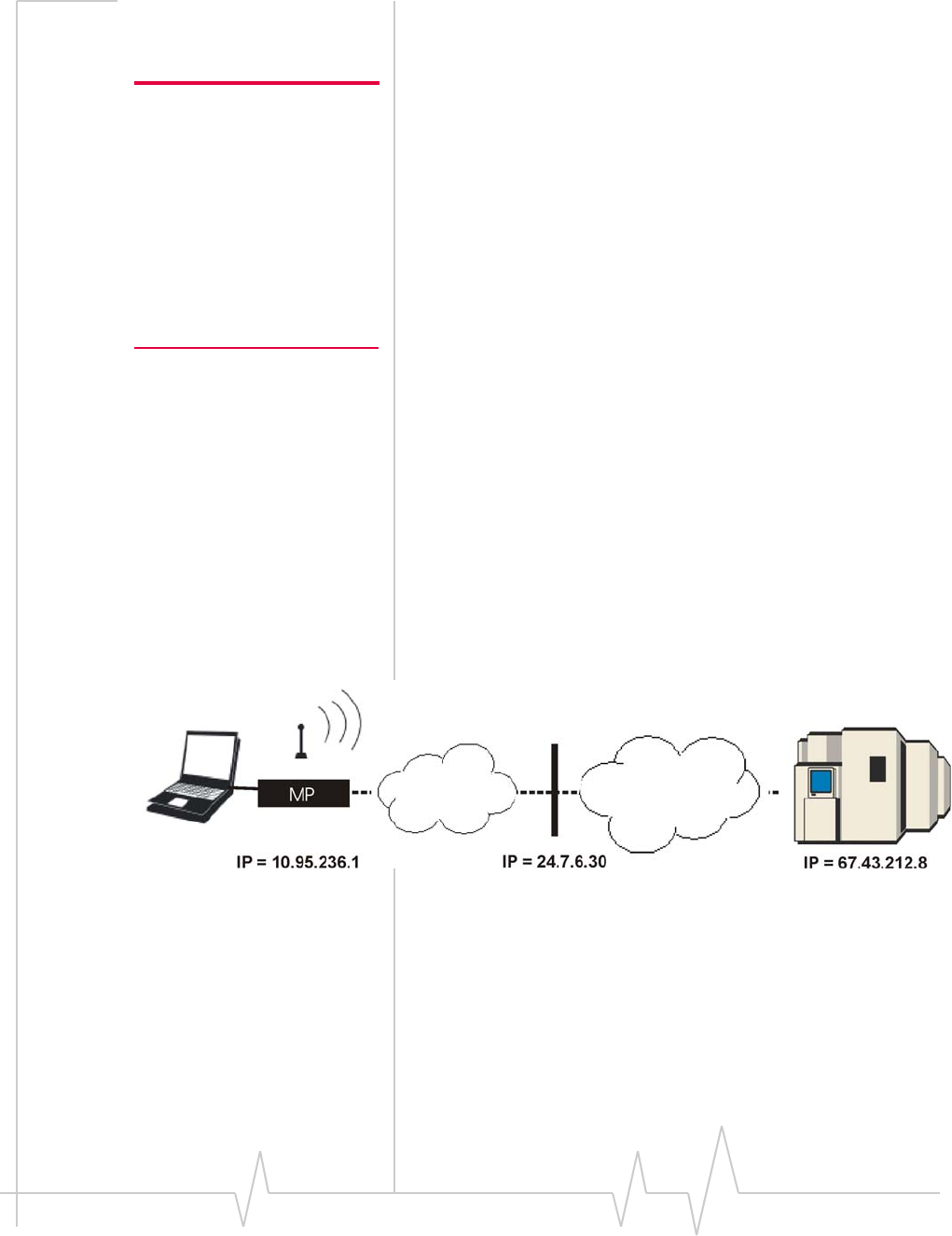
Assume,forexample,anMPmodemisregisteredona
network.TheMPmodemisassignedaprivateIPaddressof
10.95.236.1.WhentheMPmodemsendsMTPdatatothe
networkserver,apublicIPaddressof24.7.6.30issubstitutedat
thegatewaytotheInternet.Whenthenetworkserver
receives
thedata,thehostapplicationisonlyawareofthepublicIP
address,24.7.6.30.However,ifthenetworkserversendsdata
backtotheIPaddress24.7.6.30,thenetworkhasnowayof
identifyingthe MPmodemforwhichitisintendedandis
unabletoroutethedata
appropriately.
Figure 7-1: An MP modem connected to a network server. In this scenario, the
IP address is “NAT’d” from 10.95.236.1 to 24.7.6.30. The network server is
only aware of the address 24.7.6.30, but if it sends data to that address the
network cannot route the data to the MP modem.
Network
Internet
Firewall


















