21
IMAGE
This menu features adjustments relating to picture position,
aspect ratio, etc.
ASPECT
This adjustment allows you to change the dimensions and
aspect ratio (relationship between width and height) of the
displayed image. There are five preset aspects available and
three personalised aspects (with user-settable parameters).
You can select a different aspect for each source: the selected
aspect ratio will be automatically called the next time the relative
source is called.
You can also select the required aspect ratio by repeatedly
pressing the
key, or by pressing and a numerical
key (1...8).
The following aspects are available.
NORMAL:
projects the image occupying the full height of the
screen while maintaining the aspect ratio of the input signal.
When the input signal aspect ratio is 4:3 black vertical bands
are displayed on the right and left of the picture.
ANAMORPHIC:
allows a 16:9 picture to be displayed correctly.
Letterbox: serves to display 4:3 letterbox image (with source
signal having black bands above and below the picture) so that
it fills the 16:9 screen and maintains the correct aspect ratio.
PANORAMIC:
this aspect stretches the 4:3 image, slightly cropping
the upper and lower parts.
Panoramic is ideal for displaying a 4:3 image on the 16:9 screen
of the Display.
PIXEL TO PIXEL:
this aspect displays the image as it is input without
adapting it to the screen.
The image is projected in the centre of the screen and if its ho
-
rizontal and/or vertical dimensions are smaller than the display,
it is bounded by vertical and/or horizontal black bands.
PEUSER 1, 2, 3
: When none of the preset formulas are suitable,
the User formulas are available, with the facility for continuous
horizontal and vertical
adjustment of picture size.
Screen Control
If an appropriate screen-masking interface is connected to the
12V output socket it is possible, for each aspect chosen, to re-
frame the screen to a variety of aspect ratios and screen sizes
(please refer to the screen manufacturer’s manual).
COLOR TEMPERATURE
Changes the colour balance of the image.
The color temperature adjustment is made by positioning the
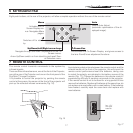
white point inside CIE cromaticity diagram.
The systems allows to choose the white point among 36 values
inside the neutral color area
(Fig. 21).
Fig. 21
The correlated color temperature varies moving along hori
-
zontal lines, low temperatures are present in the right side
(where the red component is increased), in the left side of the
diagram you can find high temperature values ( in which blue
component is higher).
The points along the lower horiziontal line represent colors that
belong to the black body curve (Fig. 22).
Along vertical lines the color temperature is constant but is
different from black body curve, which mean if you select
point from the high part of the diagram you increase the green
componet, while low part of diagram cause an increase of
purple component.
Red
Green
Blu