Warning: The new host must use the same byte order as the old host. If it does
not, you cannot access the deduplicated data.
(In computing, endianness describes the byte order that represents data: big
endianand littleendian. For example,Sun SPARCprocessors andIntel processors
use different byte orders. Therefore, you cannot replace a Solaris SPARC host
with a host that has an Intel processor.
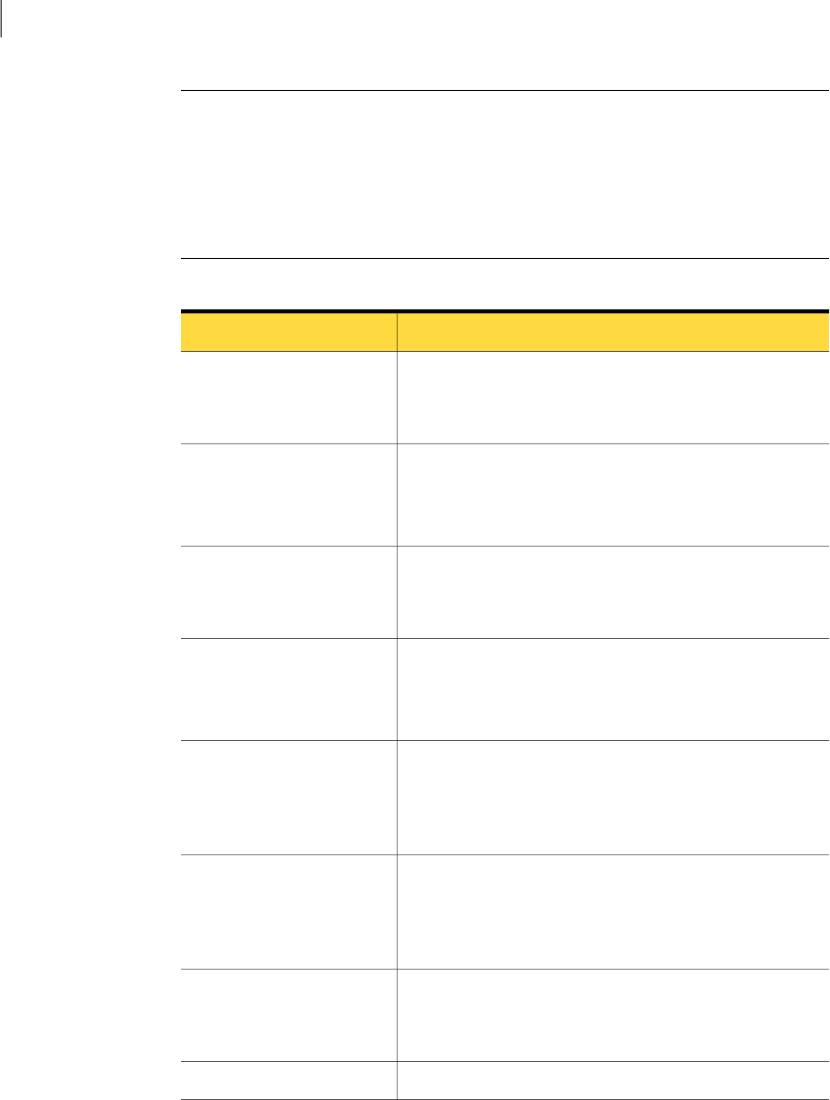
Table 8-2
Process to recover from a permanent media server failure
ProcedureTask
See “Changing the deduplication disk volume state”
on page 77.
See “Changing the deduplication pool state” on page 77.
Changethediskvolumestate
anddisk poolstateto DOWN
Use the same host name as the failed server.
See “About deduplication servers” on page 21.
See“Aboutdeduplicationserverrequirements”on page23.
Configure the new host so it
meets deduplication
requirements
Ensure that the storage and database are mounted at the
same locations.
See the storage vendor's documentation.
Move the storage to the new
host.
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for UNIX and Linux.
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for Windows.
See “About the deduplication license key” on page 42.
Install the NetBackup media
server software on the new
host
If you have load balancing servers, delete the NetBackup
Deduplication Engine credentials on those media servers.
See “Deleting credentials from a load balancing server”
on page 75.
Delete the credentials on
media servers
AddtheNetBackupDeduplicationEnginecredentialstothe
storage server.
See “Adding NetBackupDeduplication Engine credentials”
on page 74.
Add the credentials to the
storage server
Ifyoudidnotsaveastorageserverconfigurationfilebefore
the failure, get a template configuration file.
See “Getting the storage server configuration” on page 68.
Get a configuration file
template
See“Editingastorageserverconfigurationfile”onpage68.Edit the configuration file
Disaster recovery
Recovering from a permanent deduplication storage server failure
106