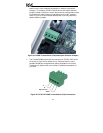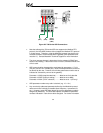
53
15.2 Modbus Plus
• Supported MSTR functions are indicated in Table 5.
Table 5: Supported MSTR Functions
Function Code Function
1 Write Registers
2 Read Registers
5 Write Global Data
6 Read Global Data
• Modbus Plus register assignments are common between the Modbus Plus
and Modbus RTU Slave protocols. In other words, when a point in the
point database has been assigned a “Modbus Slave” register index, both
Modbus Plus and Modbus RTU Slave protocols will access that point’s
value by referencing the same register index.
• Configuration tip: Improved network utilization may be obtained by
appropriately grouping points into blocks having contiguous “Modbus
Slave” register assignments. In this way, the “read registers” and “write
registers” functions can be used to perform transfers of larger blocks of
registers using fewer Modbus Plus transactions compared to a situation
where the read/write registers were arranged in an alternating or scattered
fashion.
• Because the transaction is handled locally within the gateway, write data
checking is not available. For example, if a write is performed to a register
with a data value that is out-of-range of the corresponding “source port”
object, no Modbus Plus exception will be immediately returned. However,
the point will always reflect the “source port” status and object value. In
other words, if such an out-of-range write attempt is performed, the
unsuccessful “source port” network write can be observed by reading the
current (unchanged) value of the point during a subsequent Modbus Plus
transaction.