90
91
Section 14. Performing Device Diagnostics
This section contains the following topics:
Conguring Port Mirroring
Viewing Integrated Cable Tests
Viewing Optical Transceivers
14.1 Conguring Port Mirroring
Port mirroring monitors and mirrors network trafc by forwarding copies of incoming and outgoing packets from one port to a
monitoring port. Port mirroring can be used as a diagnostic tool as well as a debugging feature. Port mirroring also enables
switch performance monitoring.
Network administrators can congure port mirroring by selecting a specic port from which to copy all packets, and other
ports to which the packets copied.
To perform port mirroring diagnostics:
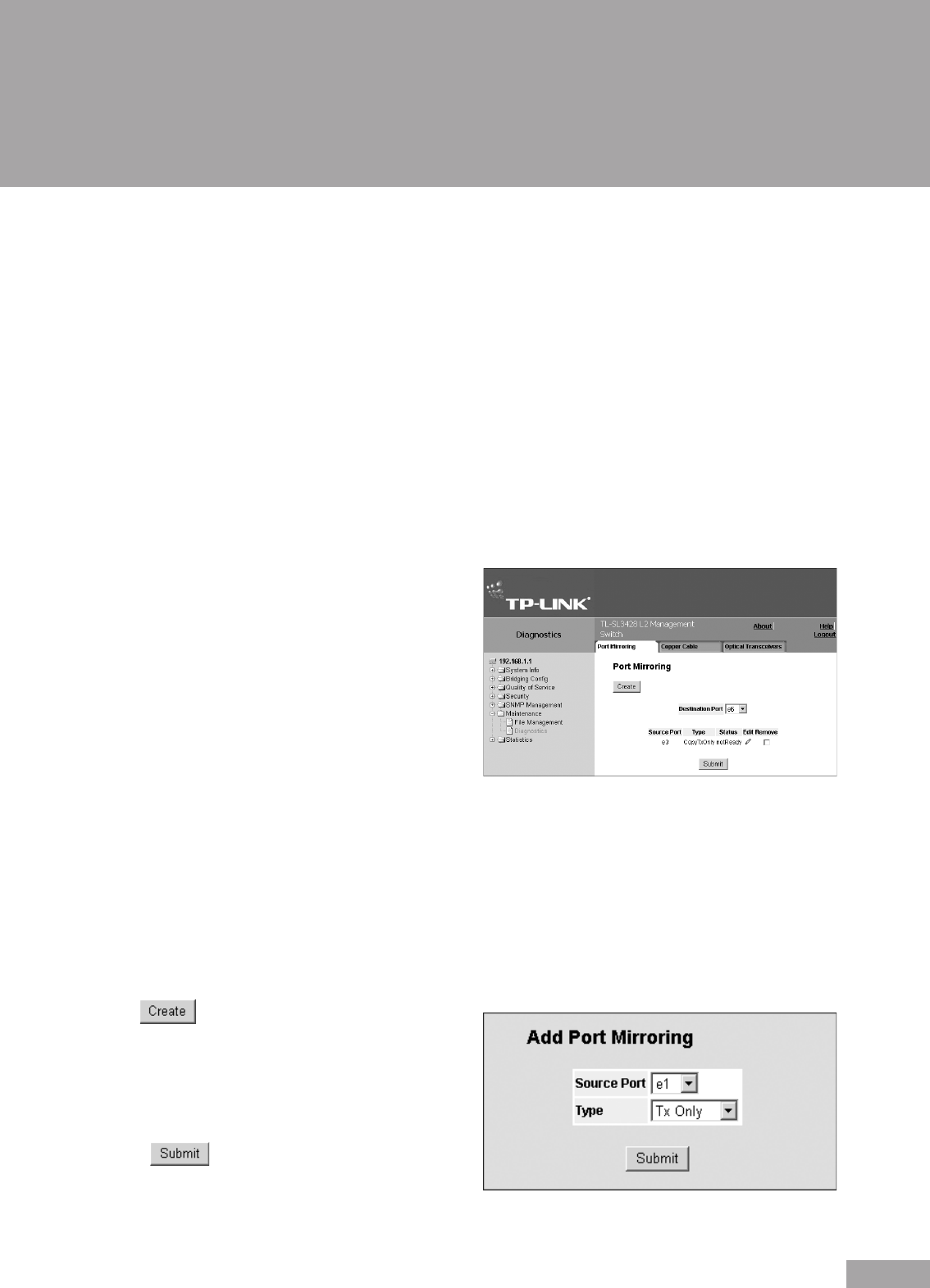
1. Click System > Maintenance > Diagnostics > Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring Page opens:
Figure 127: Port Mirroring Page
The Port Mirroring Page contains the following elds:
Destination Port — Denes the port number to which
port trafc is copied.
Transmit Packets — Denes the how the packets are
mirrored. The possible eld values are:
– Untagged — Mirrors packets as untagged VLAN
packets. This is the default value.
– Tagged — Mirrors packets as tagged VLAN packets.
Source Port — Indicates the port from which the packets are mirrored.
Type — Indicates the port mode conguration for port mirroring. The possible eld values are:
– RX — Denes the port mirroring on receiving ports.
– TX — Denes the port mirroring on transmitting ports.
– Both — Denes the port mirroring on both receiving and transmitting ports. This is the default value.
Remove — Removes the port mirroring session. The possible eld values are:
– Checked — Removes the selected port mirroring sessions.
– Unchecked — Maintains the port mirroring session.
2. Click . The Add Port Mirroring Page opens:
Figure 128: Add Port Mirroring Page
3. Select a port in the Source Port eld.
4. Select a port type in the Type eld.
5. Click . The port mirroring session is dened,
and the device is updated.
