363
convenient for load balance and route backup. However, it also has its own defects. Static
route, as its name indicates, is static. It won’t modify the route automatically on network
failure, and manual configuration is required on such occasions, therefore it is not suitable
for mid and large-scale networks.
Static route is mainly used for the following two conditions: 1) in stable networks to reduce
load of route selection and routing data streams. For example, static route can be used in
route to STUB network. 2) For route backup, configure static route in the backup line, with
a lower priority than the main line.
Static route and dynamic route can coexist; layer3 switch will choose the route with the
highest priority according to the priority of routing protocols. At same time, static route can
be introduced (redistribute) in dynamic route, and change the priority of the static route
introduced.
15.2.2 Introduction to Default Route
Default route is a static route, which is used only when no matching route is found. In the
route table, default route in is indicated by a destination address of 0.0.0.0 and a network
mask of 0.0.0.0, too. If the route table does not have the destination of a packet and has
no default route configured, the packet will be dropped, and a ICMP packets will be sent to
the source address indicate the destination address or network is unreachable.
15.2.3 Static Route Configuration
15.2.3.1 Static Route Configuration Task Sequence
1. Static Route Configuration
2. Default Route Configuration
1. Static Route Configuration
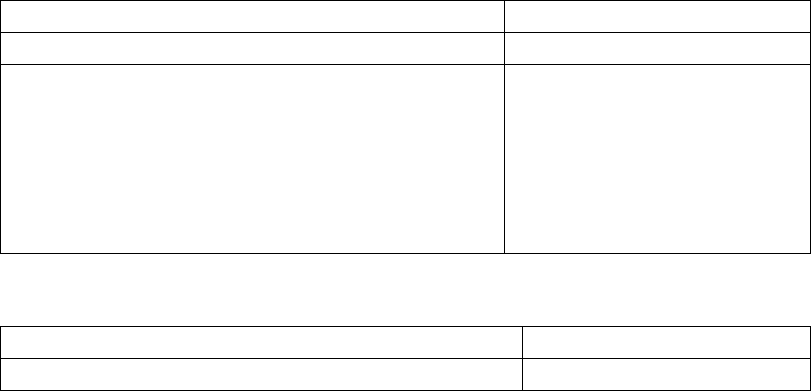
Command Explanation
Global Mode
ip route <ip_address> <mask> <gateway>
[<preference>]
no ip route <ip_address> <mask> <gateway>
[<preference>]
Configures a static route;
the “no ip route
<ip_address> <mask>
<gateway> [<preference>]”
command deletes a static
route entry.
2. Default Route Configuration
Command Explanation
Global Mode


















