74
B
IP Address Setup
The DSL-G604T is designed to provide network administrators maximum flexibility for IP addressing on the
Ethernet LAN. The easiest IP setup choice in most cases is to let the Router do it using DHCP, which is enabled
by default. This appendix briefly describes various options including DHCP, used for IP setup on a LAN. If you
are new to IP networking, the next appendix provides some background information on basic IP concepts.
Assigning Network IP Addresses
The IP address settings, which include the IP address, subnet mask and gateway IP address are the first and most
important internal network settings that need to be configured. The Router is assigned a default LAN IP address
and subnet mask. If you do not have a preexisting IP network and are setting one up now, using the factory
default IP address settings can greatly ease the setup process. If you already have a preexisting IP network, you
can adjust the IP settings for the Router to fit within your existing scheme.
Using the Default IP Address
The Router is shipped with a preset default IP address setting of 192.168.1.1 for the LAN port. There are two
ways to use this default IP address, you can manually assign an IP address and subnet mask for each PC on the
LAN or you can instruct the Router to automatically assign them using DHCP. The simplest method is to use
DHCP. The DHCP function is active by default.
Manual IP Address Assignment
Manually configuring IP settings for the LAN means you must manually set an IP address, subnet mask and IP
address of the default gateway (the Router’s IP address) on each networked computer. The example listed below
describes IP configuration for computers running Windows 95 or Windows 98. Regardless of what operating
system is used on each workstation, the three network IP settings must be defined so the network interface used
by each workstation can be identified by the Router, and vice versa. For detailed information about configuring
your workstations IP settings, consult the user’s guide included with the operating system or the network
interface card (NIC).
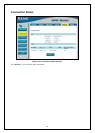
1. In Windows 95/98, click on the Start button, go to Settings and choose Control Panel.
2. In the window that opens, double-click on the Network icon.
3. Under the Configuration tab, select the TCP/IP component and click Properties.
4. Choose the Specify an IP address option and edit the address settings accordingly. Consult the table below
for IP settings on a Class C network.
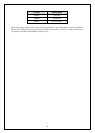
Using Default IP without DHCP
Host IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway IP
Router
192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Computer #1
192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Computer #2
192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Computer #3
192.168.1.4 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
IP Setup - Example #1
Please note that when using the default IP address as in the above example, the first three numbers in the IP
address must always be the same with only the fourth number changing. The first three numbers define the
network IP address (all machines must belong to the same IP network), while the last number denotes the host IP
address (each computer must have a unique address to distinguish it on the network). The IP address scheme
used in Example #1 can be used for any LAN that requires up to 253 separate IP addresses (excluding the