76
C
IP Concepts
This appendix describes some basic IP concepts, the TCP/IP addressing scheme and shows how to assign IP
Addresses.
When setting up the Router, you must make sure it has a valid IP address. Even if you will not use the WAN port
(ADSL port), you should, at the very least, make sure the Ethernet LAN port is assigned a valid IP address. This
is required for telnet, in-band SNMP management, and related functions such as “trap” handling and TFTP
firmware download.
IP Addresses
The Internet Protocol (IP) was designed for routing data between network sites all over the world, and was later
adapted for routing data between networks within any site (often referred to as “subnetworks” or “subnets”). IP
includes a system by which a unique number can be assigned to each of the millions of networks and each of the
computers on those networks. Such a number is called an IP address.
To make IP addresses easy to understand, the originators of IP adopted a system of representation called “dotted
decimal” or “dotted quad” notation. Below are examples of IP addresses written in this format:
201.202.203.204 189.21.241.56 125.87.0.1
Each of the four values in an IP address is the ordinary decimal (base 10) representation of a value that a
computer can handle using eight “bits” (binary digits — 1s and 0s). The dots are simply convenient visual
separators.
Zeros are often used as placeholders in dotted decimal notation; 189.21.241.56 can therefore also appear as
189.021.241.056.
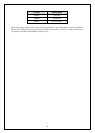
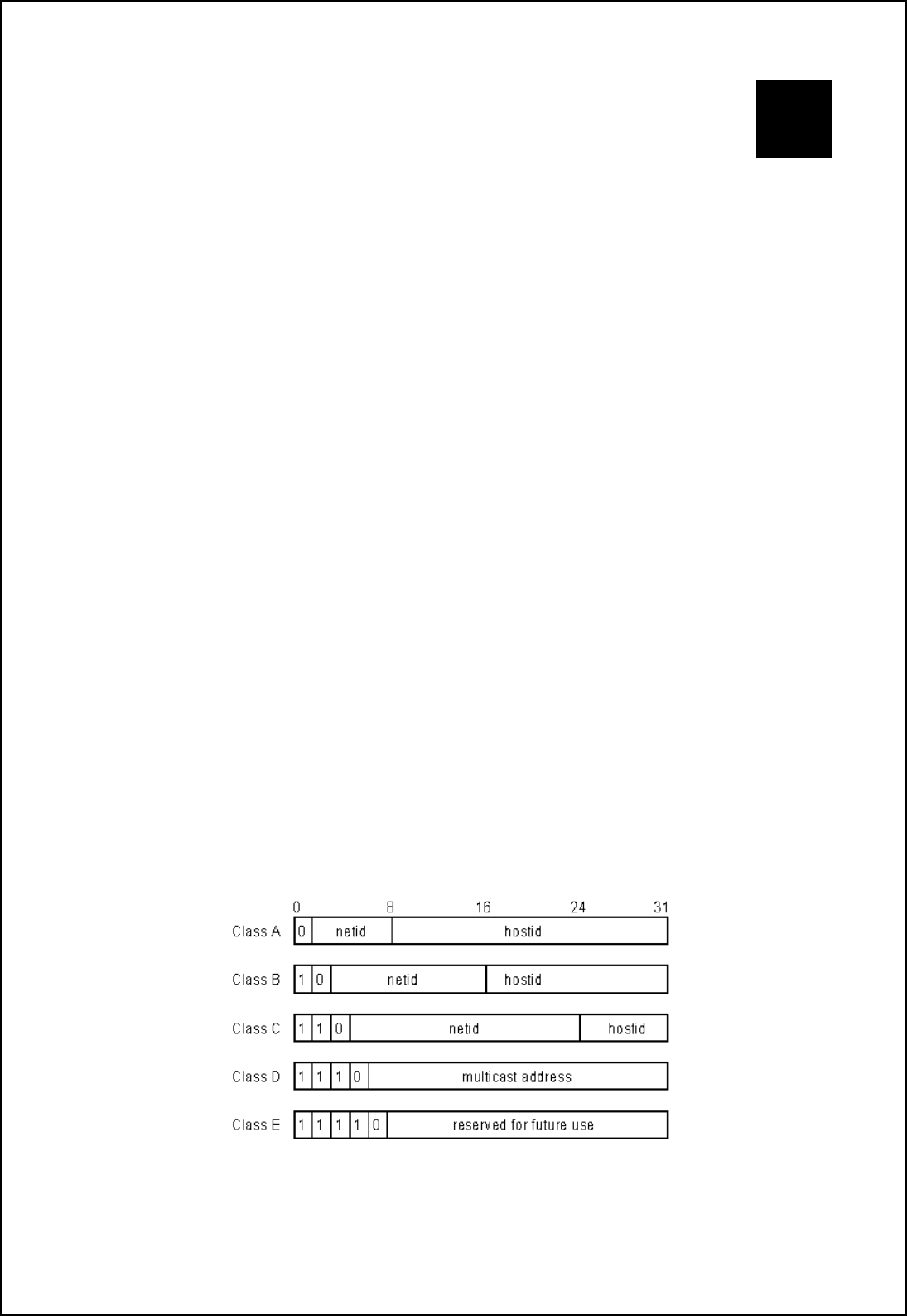
IP networks are divided into three classes on the basis of size. A full IP address contains a network portion and a
“host” (device) portion. The network and host portions of the address are different lengths for different classes of
networks, as shown in the table below.
Networks attached to the Internet are assigned class types that determine the maximum number of possible hosts
per network. The previous figure illustrates how the net and host portions of the IP address differ among the
three classes. Class A is assigned to networks that have more than 65,535 hosts; Class B is for networks that
have 256 to 65534 hosts; Class C is for networks with less than 256 hosts.