4--3Description of Operation
Closed–Transition Automatic Transfer (4ACTS, 7ACTS, 7ACTB)
The 4ACTS, 7ACTS, and 7ACTB provides load transfer in either closed (make–befo-
re–break) or open (break–before–make) transition modes depending upon the condition
of the two power sources. Control logic a utomatically determines whether the load trans-
fer should be open or closed transiti on. If both
sources are acceptable, such as during a
transfer test or when retransferring back to Normal, closed–transition transfer occurs
without interrupting t he electrical loads. If ei ther source is not
present, such as when nor-
mal fails, open–transition load transfer occurs in the break–before–make mode.
Open–Transition Load Transfer to Emergency Source
due to Normal Source Failure
The sequence for ope n–transition load transfer to the emergency source begins
automatically when the controller detects an unacceptable normal source. The Normal
source is considered unacceptable wh en any one of s ix v oltage, frequency, or phase
rotation abnormal conditions occur (see page 3–1).
Normal Source Failure. An under voltage condition on any phase of the normal source
means that the voltage has fallen below the preset dropout point.
The controller begins the load transfer sequence by de–energizing the SE and SE2 relays
and starting the Feature 1C time delay. Feature 1C time delay on engine starting prevents
nuisance starting of t he engine–generator set and load transfer to emergency due to
momentary failures of the normal source. If the normal source is restored (voltage returns
above the dropout point) while Feature 1C time delay is running, the SE a nd SE2 relay s
are re–energized and the transfer sequence is terminated. (For transfer test the Feature
1C time delay is bypassed.)
Engine Start Signal. When the Feature 1C time delay ends, the controller de–energizes
the NR relay which signals the engine–generator to start . The controller monitors the
emergency source, waiting for it to become acceptable. Both
voltage and frequency must
reach preset pickup points before the emergency source is accepted. Usually about 10
seconds elapse from dropout of the NR relay to acceptance of the emergency source. This
interval occurs because the engine–generator must crank, start, and run up to nominal
pickup poi nts. If the emergency source is available immediately, the controller will accept
it as soon as the NR relay drops out.
When the emergency source becomes acceptable, the controller starts the F eature 2B time
delay on transfer to emergency (if desired). If the emergency source fails while Feature 2B
time delay is running, the controller again waits for the emergency source to become
acceptable again and restarts Feature 2B.
At the conclusion of the Feature 2B time delay, the controller is ready to transfer the load
to emergency. If enabled, Feature 31F time delay will run prior to transfer and the Feature
31F output will be active while the time delay runs.
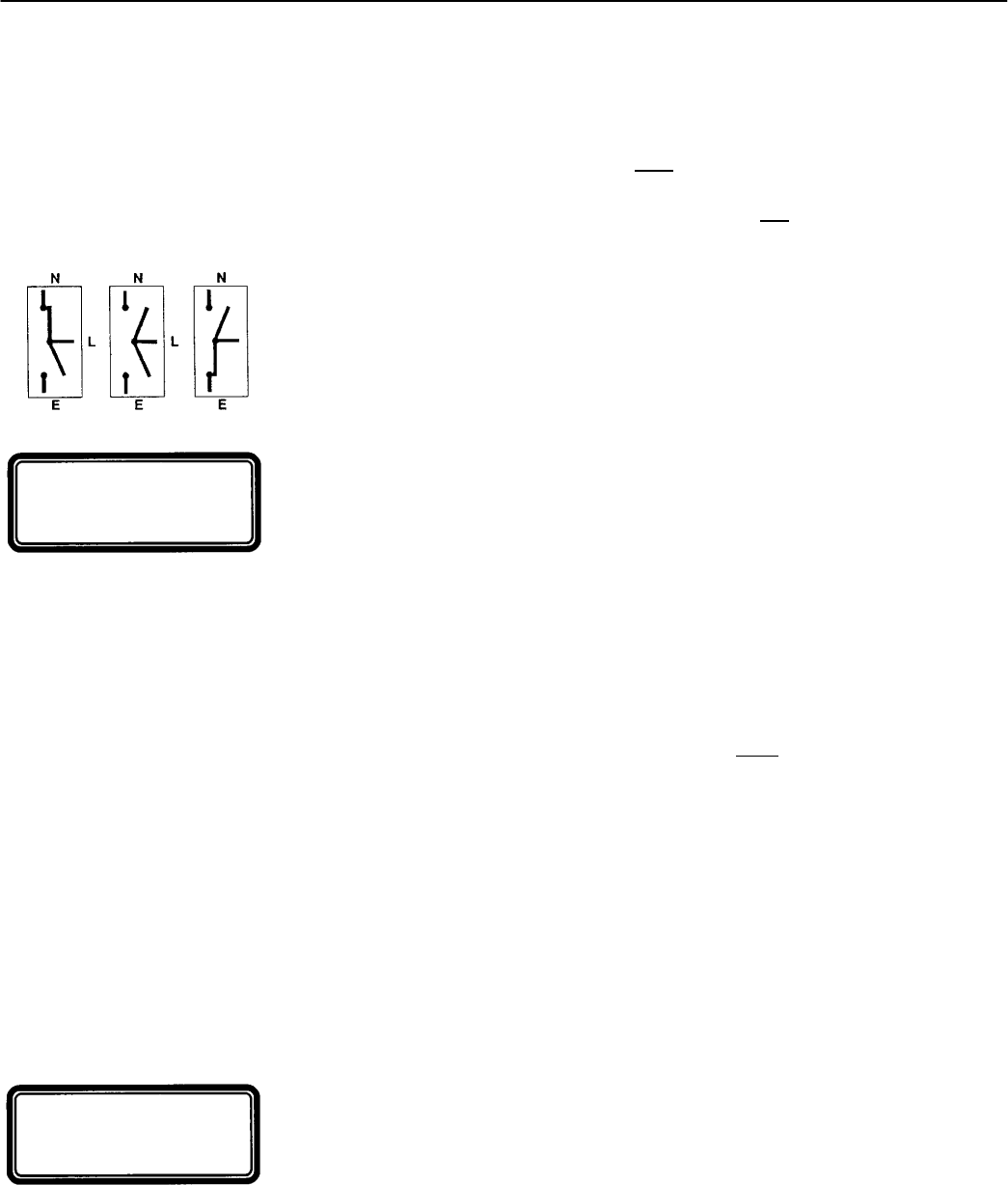
Load Transfer. To transfer the load to the emergency source the controller energizes the
ER relay. The transfer switch CN coil energizes, and all CN transfer switch contacts
(mains, controls, auxiliaries) reverse position to disconnect the Normal source. Then the
controller energizes the ER2 relay. The transfer switch CE coil energizes, and all CE
transfer switch contacts (mains, controls, auxiliaries) reverse position to connect the
Emergency source. The transfer swi tch is now supplying the load from emergency source.
If enabled, Feature 31M time delay will run after the transfer and the Feature 31M output
will be active while the time delay runs.
NORMAL FAILED
TEST MODE
TEST CIRCUIT 5
Load on Emerg