10-2 Using the Finance Solver
Financial calculations involving compound interest
include savings accounts, mortgages, pension funds,
leases, and annuities.
Time Value of Money (TVM) calculations, as the name
implies, make use of the notion that a dollar today will be
worth more than a dollar sometime in the future. A dollar
today can be invested at a certain interest rate and
generate a return that the same dollar in the future cannot.
This TVM principle underlies the notion of interest rates,
compound interest and rates of return.
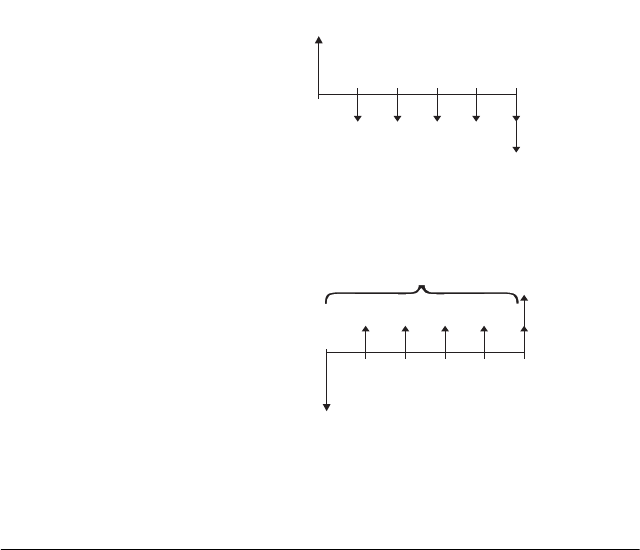
TVM transactions can be represented by using cash flow
diagrams. A cash flow diagram is a time line divided into
equal segments representing the compounding periods.
Arrows represent the cash flows, which could be positive
(upward arrows) or negative (downward arrows),
depending on the point of view of the lender or borrower.
The following cash flow diagram shows a loan from a
borrower's point of view:
On the other hand, the following cash flow diagram
shows a load from the lender's point of view:
In addition, cash flow diagrams specify when payments
occur relative to the compounding periods: at the
beginning of each period or at the end. The Finance
Solver application provides both of these payment
Present value (PV)
(Loan)
Money
received is
a positive
number
Money
paid out is
a negative
number
Equal periods
1
23
4
5
(PMT)
Future value
(FV)
Equal payments
Payment
(PMT)
Payment
(PMT)
Payment
(PMT)
Payment
(PMT)
}
}
}
}
}
FV
Equal payments
1
23
4
5
}
}
}
}
PMT
}
PMT PMT PMT PMT
Equal periods
PV
Loan
}


















