Lists 14-7
• If Decimal Mark in Modes is set to Comma, use
periods to separate arguments. For example,
CONCAT(L1.L2).
Common operators like +, –, ×, and / can take lists as
arguments. If there are two arguments and both are lists,
then the lists must have the same length, since the
calculation pairs the elements. If there are two arguments
and one is a real number, then the calculation pairs the
number with each element of the list.
Example
5*{1,2,3} returns {5,10,15}.
Besides the common operators that can take numbers,
matrices, or lists as arguments, there are commands that
can only operate on lists.
CONCAT Concatenates two lists into a new list.
CONCAT(list1,list2)
Example
CONCAT({1,2,3},{4}) returns {1,2,3,4}.
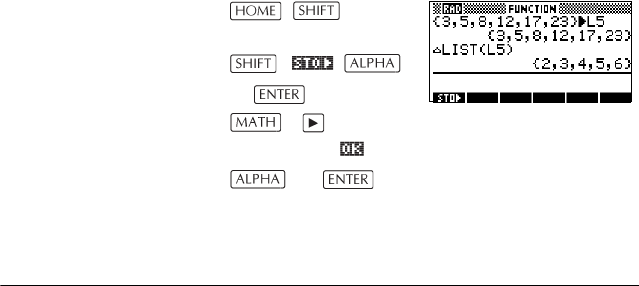
∆
LIST Creates a new list composed of the first differences, that
is, the differences between the sequential elements in
list1. The new list has one fewer elements than list1. The
first differences for {x
1
x
2
... x
n
} are {x
2
–x
1
... x
n
–x
n–1
}.
∆LIST(list1)
Example
In HOME, store {3,5,8,12,17,23} in L5 and find the first
differences for the list.
{3,5,8,12,17,23
}
L 5
L
Select ∆LIST
L5


















