aggregate the individual files into large individual files before moving them into the HPSS name
space.
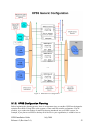
The following planning steps must be carefully considered for the HPSS infrastructure configuration
and the HPSS configuration phases:
1. Identify the site’s storage requirements and policies, such as the initial storage system size,
anticipated growth, usage trends, average file size, expected throughput, backup policy, and
availability. For more information, see Section 3.2: Requirements and Intended Uses for
HPSS on page 56.
2. Define the architecture of the entire HPSS system to satisfy the above requirements. The
planning should:
• Identify the nodes to be configured as part of the HPSS system.
• Identify the disk and tape storage devices to be configured as part of the HPSS system
and the nodes/networks to which each of the devices will be attached. Storage devices
can be assigned to a number of nodes to allow data transfers to utilize the devices in
parallel without being constrained by the resources of a single node. This capability
also allows the administrator to configure the HPSS system to match the device
performance with the network performance used to transfer the data between the
HPSS Movers and the end users (or other HPSS Movers in the case of internal HPSS
data movement for migration and staging). Refer to Section 3.4 : Hardware
Considerations on page 62 for more discussions on the storage devices and networks
supported by HPSS.
• Identify the HPSS subsystems to be configured and how resources will be allocated
among them. Refer to Section 3.8: Storage Subsystem Considerations on page 94 for
more discussion on subsystems.
• Identify the HPSS servers to be configured and the node where each of the servers
will run. Refer to Section 3.7: HPSS Server Considerations on page 80 for more
discussions on the HPSS server configuration.
• Identify the HPSS user interfaces (e.g. FTP, PFTP, Client API) to be configured and
the nodes where the components of each user interface will run. Refer to Section 3.6:
HPSS Interface Considerations on page 79 for more discussion on the user interfaces
supported by HPSS.
3. Ensure that the prerequisite software has been obtained, installed, and configured properly in
order to satisfy the target HPSS architecture. Refer to Section 3.3: Prerequisite Software
Considerations on page 58 for more information on the HPSS prerequisite software
requirements.
4. Determine the DB2 disk storage space needed to satisfy the requirements of the HPSS
system, and verify there is sufficient free space in the file systems to meet those needs. Refer
to Section 3.5.4: HPSS Metadata Space on page 74 for more discussions of metadata sizing
requirements.
5. Verify that each of the identified nodes has sufficient resources to handle the work loads to
be imposed on the node. Refer to Section 3.5.5: System Memory and Disk Space on page 78
for more discussions on the system resource requirements.
6. Plan the design of the HPSS storage characteristics and HPSS storage space to satisfy the
site’s requirements:
• Plan for file families, if any. Refer to Section 3.10.4: File Families on page 112 for
HPSS Installation Guide July 2008
Release 6.2 (Revision 2.0) 53