15
Using the Intel Express 460T Standalone Switch
CHAPTER 2
Using the 460T
Tagged Frames
The 802.1D (1998 Edition) and 802.1Q specifications published by the IEEE
(Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) extended Ethernet
functionality to add tag information to Ethernet frames and propagate these
tagged frames between bridges (for example, a switch). The tag can carry
priority information, VLAN information, or both and enables bridges to
intelligently direct traffic across the network.
Priority
The IEEE 802.1D (1998 Edition) specification incorporates IEEE 802.1p and
defines information in the frame tag to indicate a priority level. When these
tagged packets are sent out on the network, the higher priority packets are
transferred first. Priority packet tagging (also known as Traffic Class
Expediting) is usually set on the LAN adapter in a PC and works with other
elements of the network (switches, routers) to deliver priority packets first.
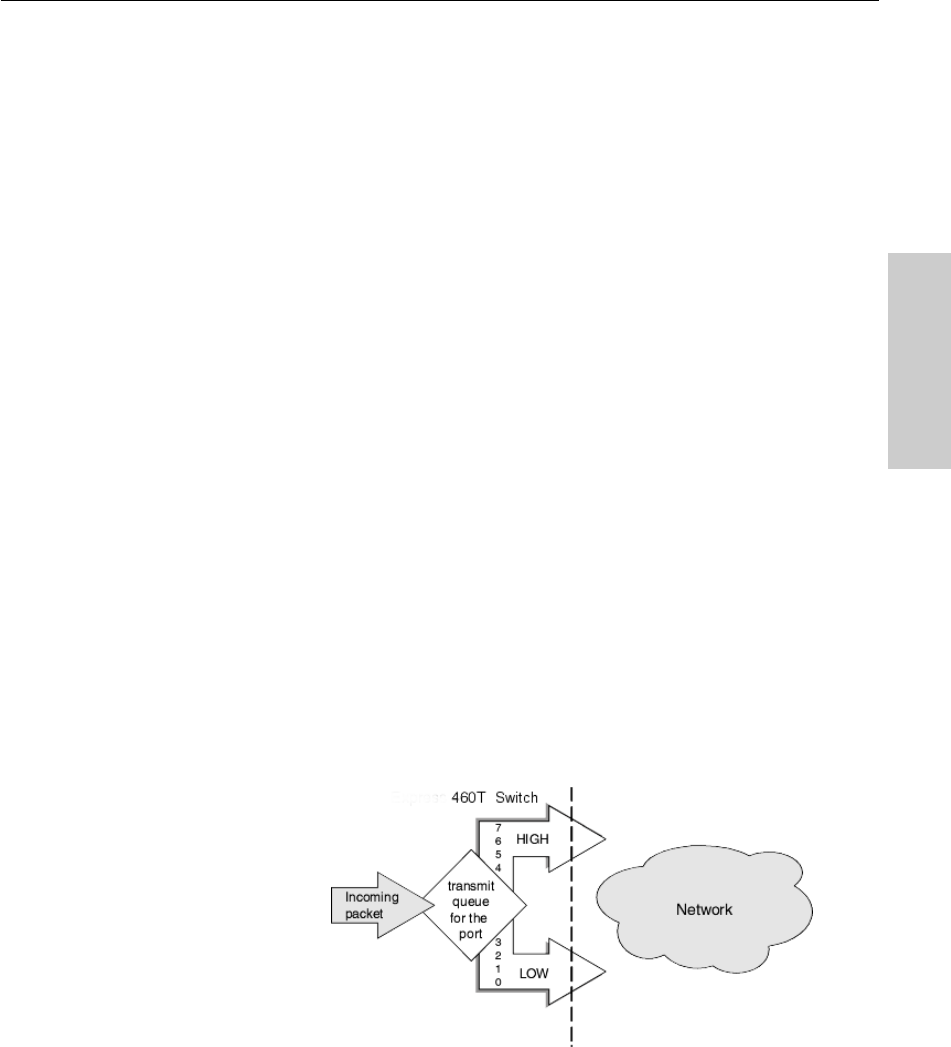
The priority level can range from 0 (low) to 7 (high).
The 460T switch can read the priority tags and forward traffic on a per port
basis. The switch uses two priority queues per port and routes traffic to a
queue depending on the packet’s tag. For example, when a packet comes
into the switch with a high-priority tag, the switch routes the packet to its
high-priority queue.
Although there are eight priority levels, the 460T switch can only route a
packet into one of the two queues. The switch maps levels 0-3 to the low
queue (which is the default) and levels 4-7 to the high queue. If a packet is
untagged, the switch determines the best way to send the packet.


















