16
CHAPTER 2
Intel Express 460T Standalone Switch Users Guide
Link Aggregation
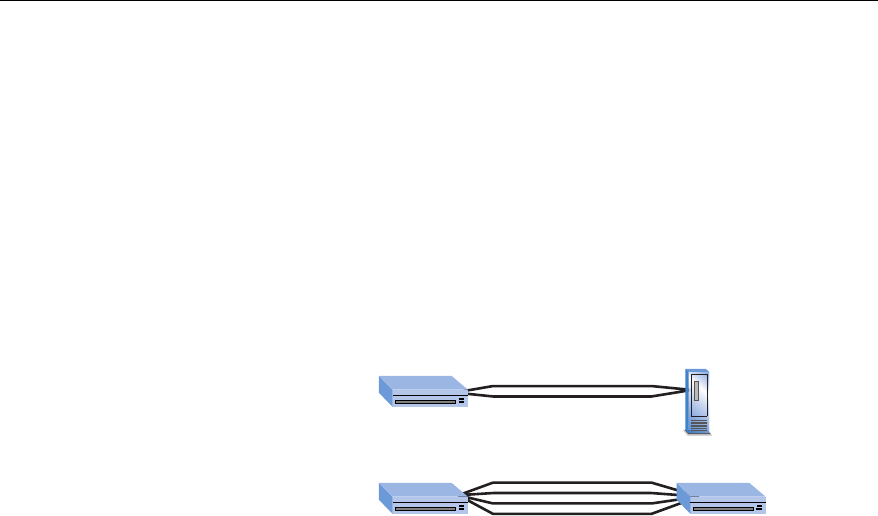
You can use link aggregation (sometimes known as port trunking) to
combine from 2 to 8 (adjacent) ports so that they function as a single high-
speed link. For example, link aggregation is useful when making connections
between switches or to connect servers to the switch.
You can also use link aggregation to increase the bandwidth to some
devices. Link aggregation can also provide a redundant link for fault
tolerance. If one link in the aggregation fails, the switch balances the traffic
among the remaining links.
2 ports aggregated x 100Mbps = 200Mbps link
4 ports aggregated x 100Mbps = 400Mbps link
To aggregate ports, you must link an “anchor” port to an adjacent port. The
460T Switch supports up to four link aggregation groups (anchor ports 1, 9,
17) for a 24-port switch and up to three link aggregation groups (anchor
ports 1, 9) on a 16-port switch. This includes one link aggregation group for
the two 100FX module ports.
Guidelines
When setting up link aggregation, remember these guidelines:
• The switch treats aggregated links as a single port. This includes
Spanning Tree and VLANs.
• All ports share the same settings as the anchor port. You can change
anchor port settings, but you cannot configure other ports in the link.
• When a port is configured as a member of an aggregated link, it
immediately adopts the characteristics of the anchor port. When a port
is no longer a member of an aggregated link, the characteristics are
reset to the default settings (autonegotiate speed/duplex, flow control
enabled).
• If a port is part of an aggregated link, it cannot be configured as the
target port for a port mirror. However, a port in an aggregated link can
serve as the source port for a port mirror.


















