Chapter 3 - MACSI Host Interface
90
Receive
The host provides the controller with Receive commands, which specify the host resources to be used for incoming
frames. As frames come in, the controller transfers them to the specified host memory locations, updates the provided
Receive commands, and posts them back to the host.
Receive commands may be allocated to particular ports, or they may be placed in a "free pool", and the controller will
use them as needed. This is done with the ANY bit in the Command Options field. A suggested practice would be to
post a minimum number of Receive commands for each port, to prevent any port from getting starved out by activity
on other ports, and then post a pool of receives to be used by all ports.
The controller will use available internal resources to buffer incoming frames, so that the host does not have to meet
tight timing windows in order to prevent dropped packets. However, receive performance will largely be a function of
how many commands may be aggregated into a single multiple completion return, which will increase as the available
number of host-supplied commands increases.
Finally, receives posted back using the multiple completion mechanism will not be separated by port number. The host
will need to scan the list of returned frames to separate out by ports, if necessary.
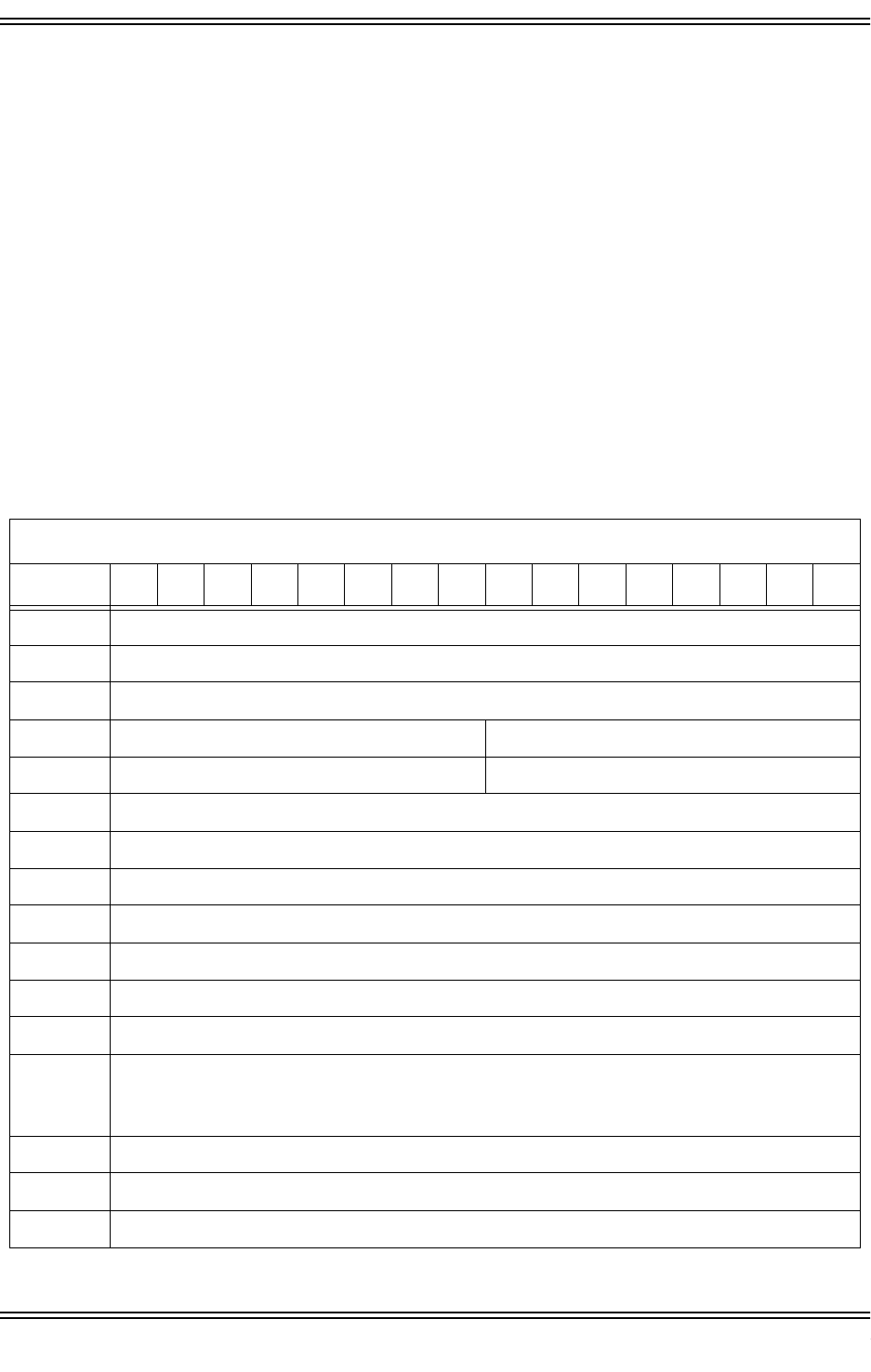
Table 3-32. Receive
Receive
Offst 1514131211109876543210
0x00 Command Code
0x01 Command Options
0x02 Return Status
0x03 Normal Completion Level Normal Completion Vector
0x04 Error Completion Level Error Completion Vector
0x05 DMA Transfer Control Word
0x06 Buffer Address (MSW)
0x07 Buffer Address (LSW)
0x08 Reserved
0x09 Max Transfer Size / Actual Transfer Size
0x0A Reserved
0x0B Packet Type / Length Field
0x0C
to
0x0E
Source Address
(6 Bytes)
0x0F Reserved
0x10 Reserved
0x11 Reserved


















