LaCie Biggest Quadra
User Manual
page 16
Understanding RAID
3. Understanding RAID
Your LaCie Biggest Quadra is shipped with a pre-
configured RAID level of 5, but it supports four dif-
ferent RAID levels: 0, 0 + 1, 5 and 5 + Hot Spare. is
section will help you decide which RAID level is right
for you.
3.1. RAID 0
Striped Disk Array Without Fault Tolerance
Also called striping, this level offers high transfer
rates and is ideal for large blocks of data where speed
is of the utmost importance. RAID 0 implements a
striped disk array, where all of the hard disks are linked
together to form one large aggregate hard disk. In this
configuration, data is broken down into blocks and each
block is written to a separate disk drive within the array;
I/O performance is greatly improved by spreading the I/
O load across several drives. In this array, however, when
one disk fails, all of the data on the array is lost.
Storage capacity is determined by the smallest disk
in the array, and the smallest disk’s capacity is applied to
all of the other disks in the array. So, for instance, if you
had four disks installed, ranging in capacity from 40GB
to 80GB, when the RAID 0 array is built your system
will see one, 160GB (40GB x 4) hard disk.
While this is a very simple and easily implemented
design, RAID 0 should never be used in mission criti-
cal environments. When even just one disk in the array
fails, all of the data on the entire array will be lost.
Characteristics and Advantages■
Data is broken down into blocks and each block
is written to a separate disk drive
I/O performance improved by spreading the load
across multiple drives
Overhead is lowered due to no calculations for
parity
Simple design and easily implemented
❖
❖
❖
❖
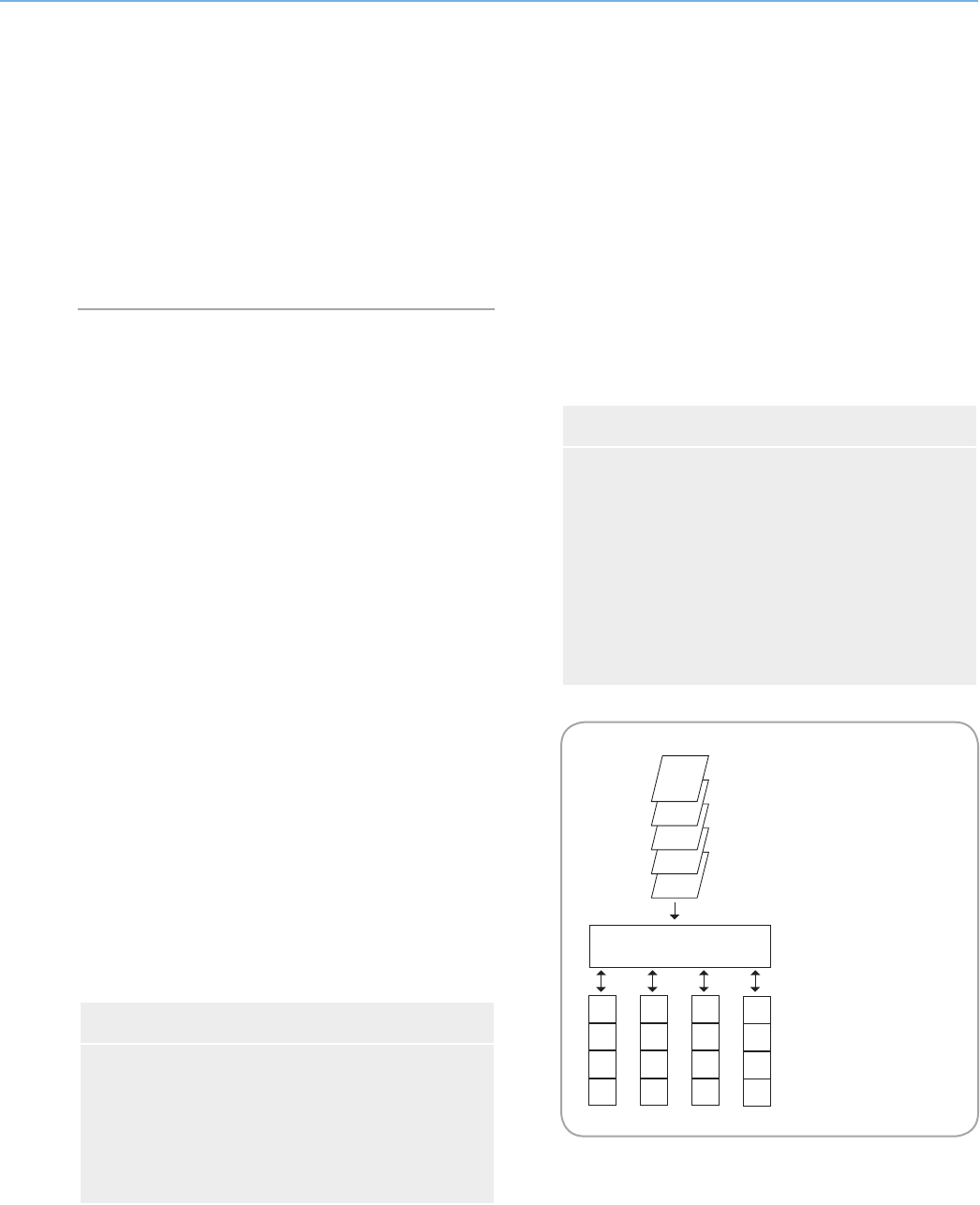
This diagram represents a
RAID 0 array, consisting of
four disks, which are
connected to the Controller.
Data blocks are distributed
across all of the disks in the
array.
A
E
I
M
B
F
J
N
C
G
K
O
D
H
L
Etc...
E
D
C
B
A
CONTROLLER
Recommended Uses■
Video production and editing
Image editing
Pre-press applications
Applications requiring high-bandwidth
❖
❖
❖
❖
Fig. 3.1.


















