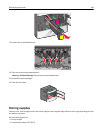
Securing the memory before moving the printer
Statement of Volatility
Your printer contains various types of memory that are capable of storing device and network settings, information
from embedded solutions, and user data. The types of memory—along with the types of data stored by each—are
described below.
• Volatile memory—Your device utilizes standard Random Access Memory (RAM) to temporarily buffer user data
during simple print and copy jobs.
• Non‑volatile memory—Your device may utilize two forms of non-volatile memory: EEPROM and NAND (flash
memory). Both types are used to store the operating system, device settings, network information, scanner and
bookmark settings, and embedded solutions.
• Hard disk memory—Some devices have a hard disk drive installed. The printer hard disk is designed for
device‑specific functionality and cannot be used for long term storage for data that is not print‑related. The hard
disk does not provide the capability for users to extract information, create folders, create disk or network file
shares, or FTP information directly from a client device. The hard disk can retain buffered user data from complex
scan, print, copy, and fax jobs, as well as form data, and font data.
There are several circumstances under which you might wish to erase the contents of the memory devices installed in
your printer. A partial list includes:
• The printer is being decommissioned
• The printer hard drive is being replaced
• The printer is being moved to a different department or location
• The printer is being serviced by someone from outside your organization
• The printer is being removed from your premises for service
• The printer is being sold to another organization
Disposing of a hard drive
Note: Not all printers have a hard disk installed.
In high‑security environments, it may be necessary to take additional steps to ensure that confidential data stored on
the printer hard disk cannot be accessed once the printer—or its hard disk—is removed from your premises. While
most data can be erased electronically, you may want to consider one or more of the following actions before disposing
of a printer or hard disk:
• Degaussing—Flushes the hard drive with a magnetic field that erases stored data
• Crushing—Physically compresses the hard disk to break component parts and render them unreadable
• Milling—Physically shreds the hard disk into small metal bits
Note: While most data can be erased electronically, the only way to guarantee that all data is completely erased is to
physically destroy each memory device on which data could have been stored.
Erasing volatile memory
The volatile memory (RAM) installed on your printer requires a power source to retain information. To erase the
buffered data, simply power down the device.
Securing the memory before moving the printer 145