EtherFast
®
Cable/DSL Firewall Router with 4-Port Switch/VPN Endpoint
119
Instant Broadband
®
Series
118
Step Two: Pinging for a Web Address
While the IP address returned above would work as your e-mail server address,
it may not be permanent. IP addresses change all the time. Web addresses, how-
ever, usually don’t. Because of this, you’re likely to have fewer problems by
configuring your system with web addresses rather than IP addresses. Follow
the instructions below to find the web address assigned to the IP address you
just pinged.
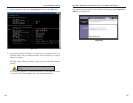
1. At the DOS command prompt, type ping -a 24.53.32.4, where 24.53.32.4
is the IP address you just pinged. Information such as the following data
will be displayed.
C:\>ping -a 24.53.32.4
Pinging mail.msnv3.occa.home.com [24.53.32.4] with
32 bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
2. Write down the web address returned by the ping command (In the
example in Figure C-2: mail.msnv3.occa.home.com is the web address).
This web address is the web address assigned to the IP address you just
pinged. While the IP address of mail could conceivably change, it is likely
that this web address will not.
3. Replace your ISP’s abbreviated server address with this extended web
address in the corresponding Internet application (web browser, e-mail
application, etc.).
Once you have replaced the brief server address with the true server address,
the Router should have no problem accessing the Internet through that Internet
application.
Figure E-2
Step One: Pinging an IP Address
The first step to determining your ISP’s web and e-mail server address is to
ping its IP address.
1. Power on the computer and the cable or DSL modem, and restore the
network configuration set by your ISP if you have since changed it.
2. Click Start, then Run, and type command. This will bring up the DOS
window.
3. At the DOS command prompt, type ping mail (assuming that the loca-
tion for which you’re trying to find an IP address is configured as mail).
Press Enter. Information such as the following data, taken from a ping of
Microsoft Network’s e-mail server, will be displayed.
C:\>ping mail
Pinging mail [24.53.32.4] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
4. Write down the IP address returned by the ping command. (In the
example above: 24.53.32.4.) This IP address is the actual IP address of the
server mail, or any other word or value you have pinged.
Figure E-1