Chapter 5: Phonebook Configuration
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. MVPGSM 58
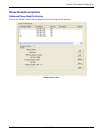
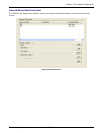
Add/Edit Outbound Phone Book: Field Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Accept Any
Number
Y/N When checked, “Any Number” appears as the value in the Destination
Pattern field.
The Any Number feature works differently depending on whether or not an
external routing device is used (Proxy for SIP protocol).
When no external routing device is used. If Any Number is selected, calls
to phone numbers not matching a listed Destination Pattern will be
directed to the IP Address in the Add/Edit Outbound Phone Book screen.
“Any Number” can be used in addition to one or more Destination Patterns.
When external routing device is used. If Any Number is selected, calls to
phone numbers not matching a listed Destination Pattern will be directed
to the external routing device used (Proxy for SIP protocol). The IP Address
of the external routing device must be set in the Phone Book Configuration
screen.
Destination
Pattern
prefixes,
area codes,
exchanges,
line numbers,
extensions
Defines the beginning of dialing sequences for calls that will be routed to a
SIP end point on the IP network. This is the phone number or beginning
portion of the phone number for calls that are to be routed to the IP
address listed below.
Total Digits as needed Number of digits the phone user must dial to reach specified destination.
This field not used in North America
Remove Prefix dialed digits Portion of dialed number to be removed before remaining digits are sent to
their destination.
Add Prefix dialed digits Digits to be added before routing the call to the address below.
IP Address n.n.n.n The IP address to which the call above will be routed with the destination
pattern given.
Description alpha-numeric This description will be sent as Caller ID information.
Protocol Type SIP Indicates protocol to be used in outbound transmission.
SIP Fields
Use Proxy Y/N Select if proxy server is used.
Transport
Protocol
TCP or
UDP
VOIP administrator must choose between UDP and TCP transmission
protocols. UDP is a high-speed, low-overhead connectionless
protocol where data is transmitted without acknowledgment,
guaranteed delivery, or guaranteed packet sequence integrity. TCP is
slower connection-oriented protocol with greater overhead, but
having acknowledgment and guarantees delivery and packet
sequence integrity.
SIP Port
Number
5060 or other
*See RFC 3087 (“Control of
Service Context using SIP
Request-URI,” by the
Network Working Group).
The SIP Port Number is a UDP logical port number. The VOIP will
“listen” for SIP messages at this logical port. If SIP is used, 5060 is the
default, standard or “well known” port number to be used. If 5060 is
not used, then the port number used is that specified in the SIP
Request URI (Universal Resource Identifier).
SIP URL sip.userphone@hostserver,
where “userphone” is the
telephone number and
“hostserver” is the domain
name or an address on the
network
Looking similar to an email address, a SIP URL identifies a user's
address.
In SIP communications, each caller or callee is identified by a SIP URL:
sip:user_name@host_name. The format of a sip URL is very similar
to an email address, except that the “sip:“ prefix is used.