3. Troubleshooting Functional Failures in Operation
41
bridge for each MST instance for route bridge, when checking the route bridge.
Table 3-14: Spanning Tree Failure Analysis Method
3.5.3 Failures on Using Ring Protocol
This subsection describes Autonomous Extensible Ring Protocol failure.
The Autonomous Extensible Ring Protocol is redundant protocol on the layer 2 network for ring topology, refer to it as
"Ring Protocol" hereafter.
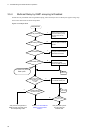
When the communication is disabled during Ring Protocol operation, follow the analysis flow to identify the symptom
No. Troubleshooting Steps and Command Action
1 Execute the show spanning-tree
command for the failed spanning tree and
check the protocol status of the spanning tree.
If shown as Enable, go to No. 2.
When tree information is not displayed while Ring Protocol and PVST+ both are
in use, go to No.7.
If shown as Disable, the spanning tree is suspended. Check the configuration.
Ring Protocol and multiple spanning tree both are used, go to No.8.
Check to see if the number of PVST+s is within the conditions of accommodation.
2 Execute the show spanning-tree
command for the failed spanning tree and
check the bridge identifier of the route bridge
for the spanning tree.
Go to No. 3 if the bridge identifier of the route bridge complies with the network
configuration.
Check the network configuration and configuration if the bridge identifier of the
route bridge does not comply with the network configuration.
3 Execute the show spanning-tree
command for the failed spanning tree and
check the port status and the port role of the
spanning tree.
Go to No. 4 if the spanning tree port status and port role comply with the network
configuration.
When the systems before Ver10.6 is used:
If the port status of the port for which the loop guard function is defined is
Blocking or Discarding, check to see if the port is a designated port. If the port is
a designated port, delete the setting of the loop guard function.
If the spanning tree port status and port role do not comply with the network
configuration, check the neighboring system status and configuration.
4 Execute the show spanning-tree
statistics command for the failed
spanning tree and check BPDU sending and
receiving on the failed port.
Check the BPDU sending/receiving counter.
[Root port]
Go to No. 5 if the BPDU receiving counter has been incremented.
If not so, BPDU may have been discarded by filtering, or BPDU may have
been discarded through bandwidth monitoring, discarding control, or shaper
of the QoS control. See "3.23.1 Checking Filtering/QoS Setting Information"
to check for it. If no problem is found, check the neighboring system.
[Designated port]
Go to No. 5 if the BPDU sending counter has been incremented. Otherwise,
see "3.4 Network Interface Communication Failure."
5 Execute the show spanning-tree
command for the failed spanning tree with
"detail" parameter specified, and check the
received BPDU bridge identifier.
Confirm that the received BPDU route bridge identifier and sending bridge
identifier comply with the network configuration. Otherwise, check the
neighboring system status.
6 Check to see if the maximum number of
failed spanning trees is within the
accommodating conditions.
Set up the number within the range of the accommodating conditions. For the
accommodating conditions, see "Configuration Settings."
7 Check to see if vlan-mapping is applied to
the single VLAN that is to operate with
PVST+.
If vlan-mapping of Ring Protocol is not applied to the target VLAN, configure it.
In addition, if multiple VLANs are applied to the vlan-mapping, review the
vlan-mapping and change it to a single VLAN.
8 Check to see if the vlan-mapping of VLANs
to be operated with MST instances is the
same as that of Ring Protocol.
If vlan-mapping of Ring Protocol is not applied to the target VLAN, adjust it to
match the configuration of VLANs with multiple spanning tree enabled.