126 ITG engineering guidelines
Enough capacity
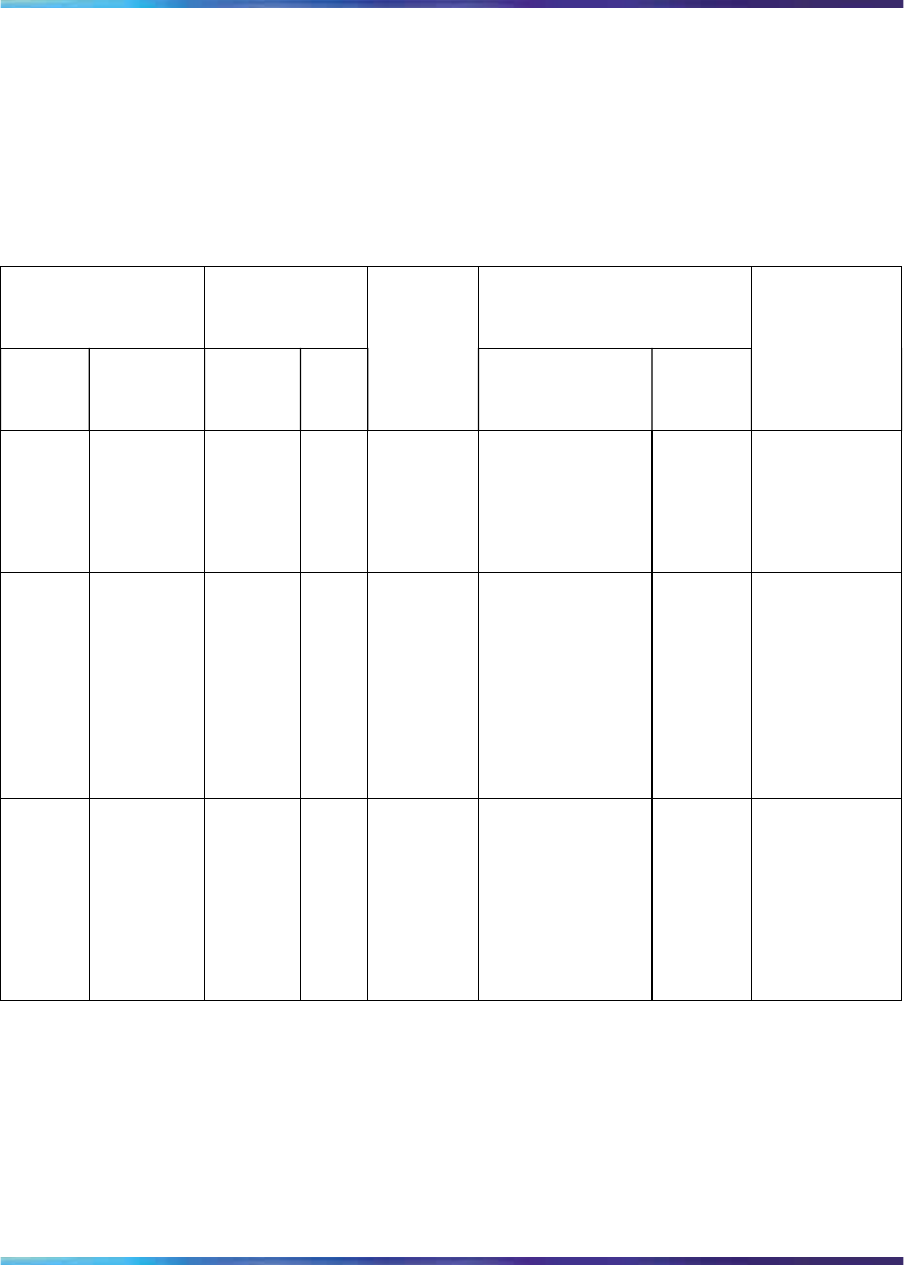
For each link, Table 23 "Computation of link capacity as compared to ITG
load" (page 126) compares the available link capacity to the additional IP
Trunk 3.01 (and later) load. For example, on link R4-R5, there is plenty
of available capacity (492 kbit/s) to accommodate the additional 24 kbit/s
of IP Trunk 3.01 (and later) traffic.
Table 23
Computation of link capacity as compared to ITG load
Link Utilization (%)
Incremental
IP Trunk 3.01 (and
later) load
End-
point
s
Capacity
(kbit/s)
Thres
hold
Use
d
Availa
ble
capacity
(kbit/s) Site pair
Traffic
(kbit/s)
Sufficient
capacity?
R1-R2
1536 80 75 76.8
Santa
Clara/Ottawa
+
Ottawa/Toky
o
21.2
Yes
R1-R4
1536 80 50 460.8
Santa
Clara/Tokyo
+ Santa
Clara/
Richardson
+
Ottawa /
Tokyo
31.4
Yes
R4-R5
1536 80 48 492
Santa
Clara/Richar
dson
+ Ottawa/
Tokyo +
Santa
Clara/Tokyo
31.4
Yes
Some network management systems have network planning modules
that compute network flows in the manner just described. These modules
provide more detailed and accurate analysis, as they can take into account
actual node, link, and routing information. They also help assess network
resilience by conducting link and node failure analysis. By simulating
failures and re-loading network and re-computed routes, the modules
indicate where the network might be out of capacity during failures.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
IP Trunk Fundamentals
NN43001-563 01.01 Standard
Release 5.0 30 May 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks
.


















