4. DSL Router Configuration Examples
6300-A2-GB20-10 November 2003
4-3
Basic Routing Configuration Example
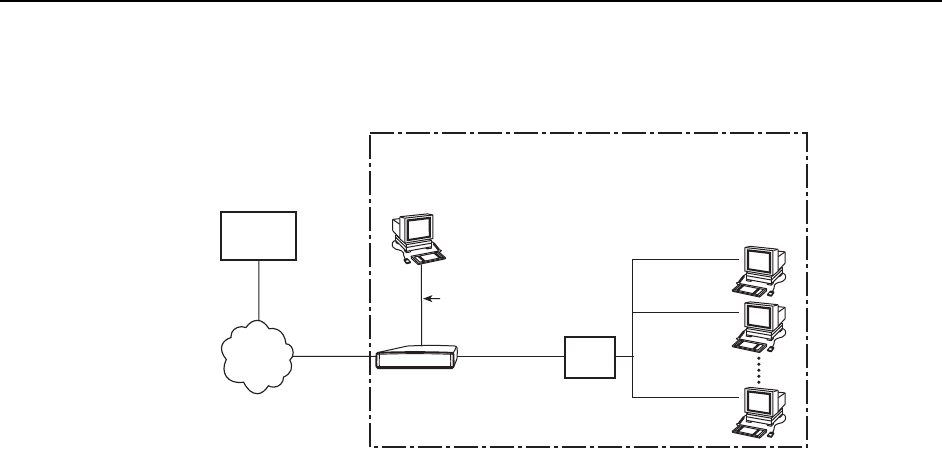
In this basic routing example:
There are multiple clients with statically assigned public IP addresses
configured on the Ethernet side of the DSL router.
The IP addresses of the clients are contained within the subnet specified by
the configured Ethernet IP address and subnet mask.
The next hop router (default gateway) of the clients is the Ethernet interface
(eth1) of the DSL router.
The next hop router for downstream forwarding from the core router is the DSL
interface (dsl1) of the DSL router.
The commands and syntax for this example are:
ip routing enable
ifn address eth1 155.1.3.254 255.255.255.0
ifn address dsl1 155.1.4.254 255.255.255.0
ip route create upstream eth1 155.1.4.1
NOTES:
— The ip routing enable command is only required when using
firmware version 4.2.5 or higher.
— FUNI/MPOA (1483 routed) link encapsulation can be used with this
configuration and the DSL card Models 8304, 8314, 8344, and 8374. Link
encapsulation is configured on the DSL port. This link encapsulation must
match the core network encapsulation type. The ip route create
upstream command is not necessary when using FUNI/MPOA link
encapsulation.
— If IP Scoping is enabled, the clients’ IP addresses must be entered into the
client VNID table.
01-16613-02
Customer Premises (CP)
DSL
Router
Hub
155.1.3.2
155.1.3.3
155.1.3.8
End-user
Systems
Console
Port
Connection
Ethernet
eth1
155.1.3.254
DSL
Core
Router
dsl1
155.1.4.254
WAN
155.1.4.1


















