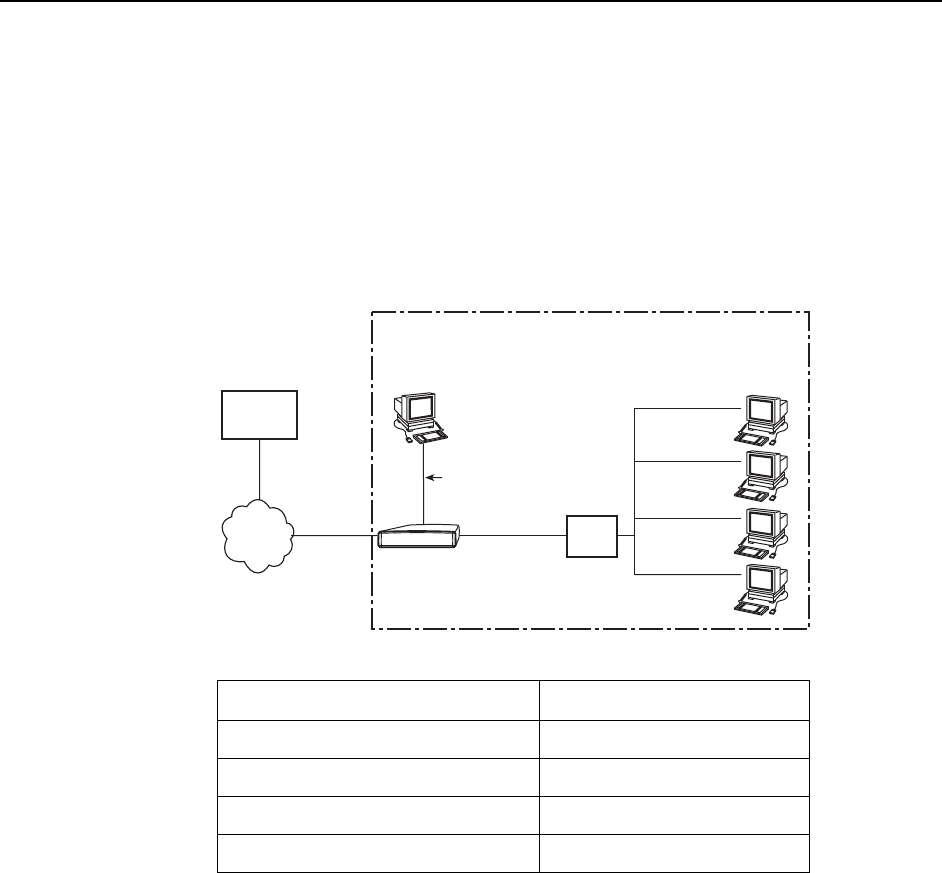
4. DSL Router Configuration Examples
4-4 November 2003 6300-A2-GB20-10
To enable Telnet through the service domain via the DSL router Ethernet (eth1)
port, use the following commands:
telnet enable
telnet login enable
telnet name create admin paradyne abc123
Basic NAT Configuration Example
In this Basic NAT example:
NAT is used for one-to-one mapping of addresses.
There are four private IP addresses configured on the Ethernet side of the
DSL router, with NAT static mappings to four public IP addresses.
The Ethernet interface (eth1) is in the private address space and the DSL
interface is in public address space.
The next hop router (default gateway) of the clients is the Ethernet IP address
of the DSL router, 10.1.3.1.
Since Basic NAT is enabled and the dsl1 interface address is on the same
subnet as the Basic NAT global IP network address, Proxy ARP must be
enabled on the DSL interface (dsl1). Proxy ARP is not necessary when using
FUNI/MPOA link encapsulation.
If IP Scoping is enabled, the client’s NAT mapping public IP addresses and the
dsl1 interface IP address must be entered into the client VNID table.
NAT Mapping Public IP Addresses Private IP Addresses
155.1.3.3 10.1.3.2
155.1.3.4 10.1.3.3
155.1.3.5 10.1.3.4
155.1.3.6 10.1.3.5
00-16767
Customer Premises (CP)
DSL
Router
Hub
10.1.3.2
10.1.3.3
10.1.3.4
End-user
Systems
Console
Port
Connection
Ethernet
eth1
10.1.3.1
DSL
Core
Router
dsl1
155.1.3.2
WAN
155.1.3.1
10.1.3.5


















