Aerobic power is enhanced in heart rate zone 3. The training intensity is higher than in sport zones 1 and
2, but still mainly aerobic. Training in sport zone 3 may, for example, consist of intervals followed by
recovery. Training in this zone is especially effective for improving the efficiency of blood circulation in
the heart and skeletal muscles.
If your goal is to compete at top potential, you will have to train in heart rate zones 4 and 5. In these
zones, you exercise anaerobically in intervals of up to 10 minutes. The shorter the interval, the higher the
intensity. Sufficient recovery between intervals is very important. The training pattern in zones 4 and 5 is
designed to produce peak performance.
The Polar target heart rate zones can be personalized by using a laboratory measured HR
max
value, or by
taking a field test to measure the value yourself. When training in a target heart rate zone, try to make use
of the entire zone. The mid-zone is a good target, but keeping your heart rate at that exact level all the
time is not necessary. Heart rate gradually adjusts to training intensity. For instance, when crossing from
heart rate target zone 1 to 3, the circulatory system and heart rate will adjust in 3-5 minutes.
Heart rate responds to training intensity depending on factors such as fitness and recovery levels, as well
as environmental factors. It is important to look out for subjective feelings of fatigue, and to adjust your
training program accordingly.
Heart Rate Variability
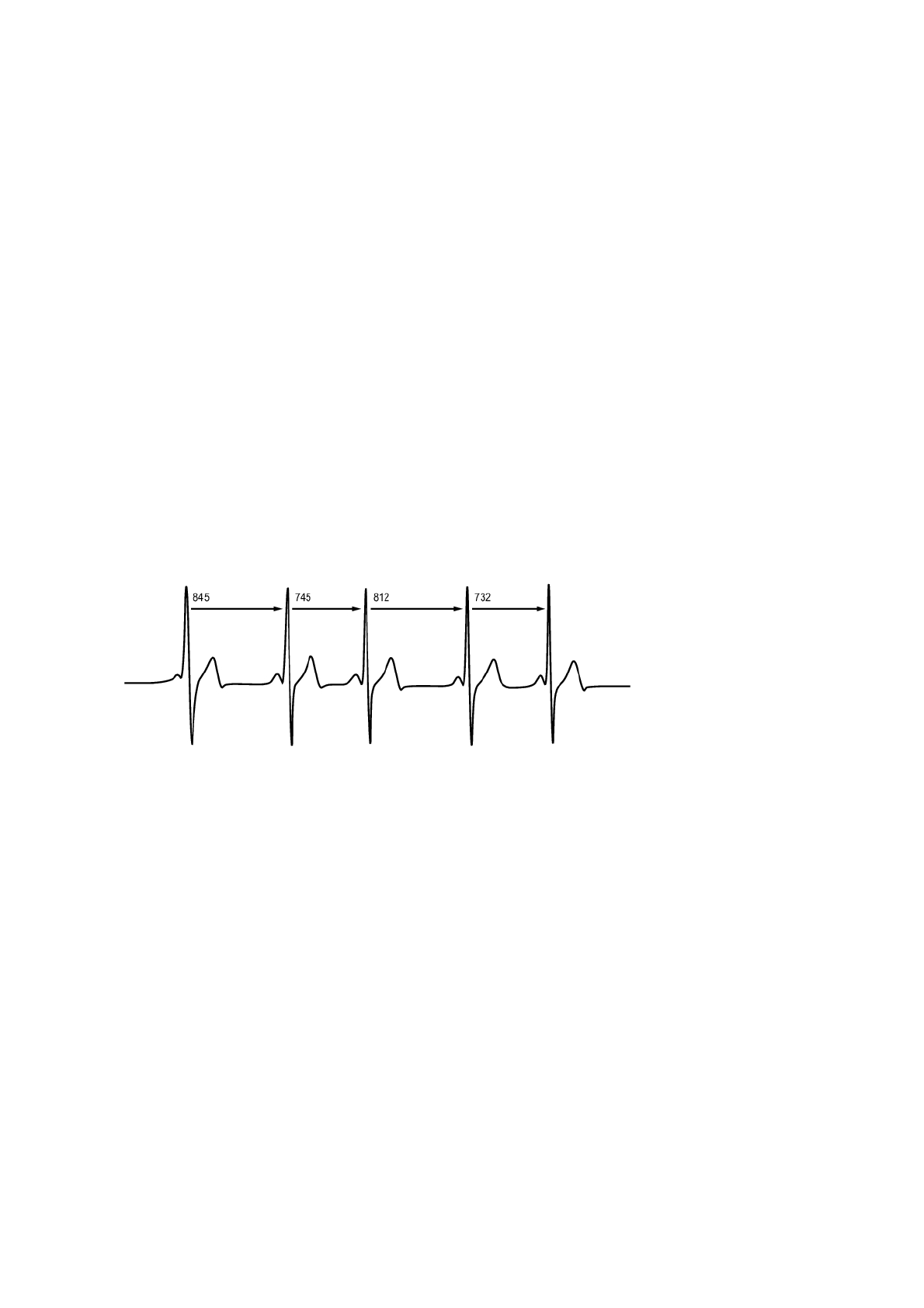
Heart rate varies with every heartbeat. Heart rate variability (HRV) is the variation of beat to beat intervals,
also known as R-R intervals.
HRV indicates the fluctuations of heart rate around an average heart rate. An average heart rate of 60
beats per minute (bpm) does not mean that the interval between successive heartbeats would be exactly
1.0 sec, instead they may fluctuate/vary from 0.5 sec up to 2.0 sec.
HRV is affected by aerobic fitness. HRV of a well-conditioned heart is generally large at rest. Other factors
that affect HRV are age, genetics, body position, time of day, and health status. During exercise, HRV
decreases as heart rate and exercise intensity increase. HRV also decreases during periods of mental
stress.
HRV is regulated by the autonomic nervous system. Parasympathetic activity decreases heart rate and
increases HRV, whereas sympathetic activity increases heart rate and decreases HRV.
HRV is used in the OwnIndex and ZoneOptimizer features.
Polar ZoneOptimizer
Polar ZoneOptimizer feature adopts this principle as it recommends lower intensity training when little
heart rate variability is detected and higher intensity training, when plenty of heart rate variability is
detected. It also gives you feedback on daily physiological status (good/normal/low) in respect to the
ENGLISH
44 Background Information


















