SuperTrak EX Series User Manual
168
Choosing a RAID Level
There are several issues to consider when choosing the RAID Level for your
logical drive. The following discussion summarizes some advantages,
disadvantages and applications for each choice.
RAID 0
Recommended applications for RAID 0:
•Image Editing
• Pre-Press Applications
• Any application requiring high bandwidth
RAID 1
Recommended applications for RAID 1:
• Accounting/Financial
•Payroll
• Any application requiring very high availability
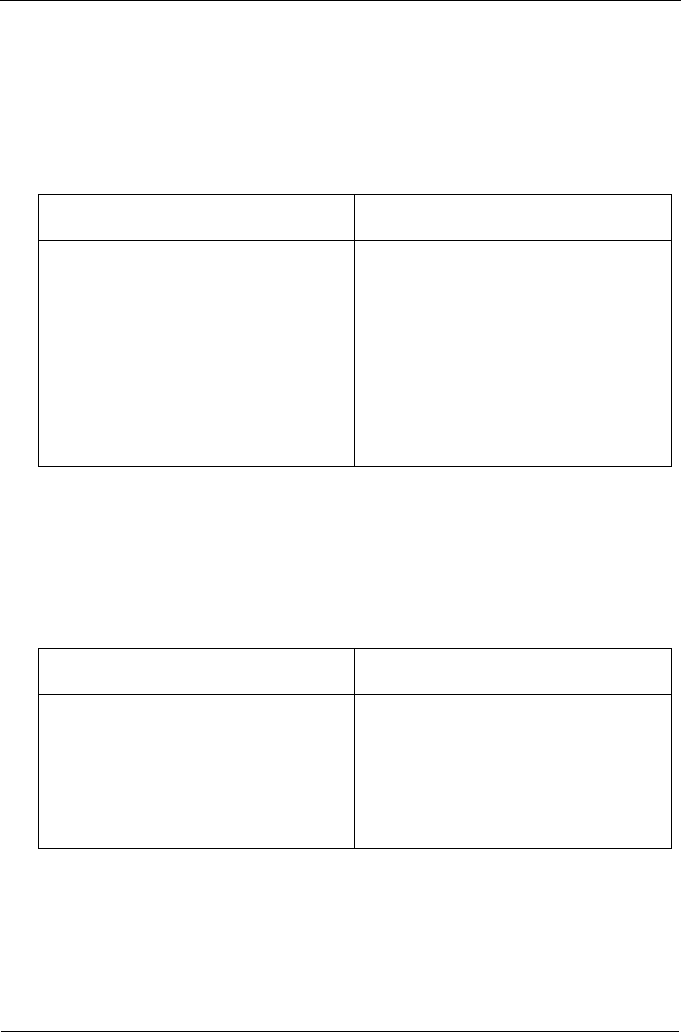
Advantages Disadvantages
Implements a striped logical drive, the
data is broken down into blocks and
each block is written to a separate
physical drive
I/O performance is greatly improved by
spreading the I/O load across many
channels and drives
No parity calculation overhead is
involved
Not a true RAID because it is not fault-
tolerant
The failure of just one drive will result
in all data in an logical drive being lost
Should not be used in mission critical
environments
Advantages Disadvantages
Simplest RAID storage subsystem
design
Can increase read performance by
processing data requests in parallel
since the same data resides on two
different drives
Very high physical drive overhead –
uses only 50% of total capacity