Operation and Maintenance Manual 23
Theory of Operation
Sulfur Chemiluminescence Detector
The Agilent model 355 Sulfur Chemiluminescence Detector (SCD) is a
sulfur-selective detector for gas chromatography. Operation of the SCD is
based on the chemiluminescence (light-producing reaction) from the reaction
of ozone with sulfur monoxide (SO) produced from combustion of the analyte:
Sulfur compound (analyte)
→ SO + H
2
O + other products
SO + O
3
→ SO
2
+ O
2
+ hη (<300–400 nm)
A vacuum pump pulls the combustion products into a reaction cell at low
pressure, where excess ozone is added. Light produced from the subsequent
reaction is optically filtered and detected with a blue-sensitive photomultiplier
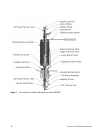
tube and the signal is amplified for display or output to a data system. Figure 1
is a pneumatic flow diagram that illustrates how the components of the system
are integrated.
The Detector has an enclosed, dedicated (Dual Plasma) Burner designed to
enhance production of the SO intermediate. This Dual Plasma Burner mounts
in the detector port of the GC. A Dual Plasma Controller provides temperature
control and gas-flow regulation to operate the Dual Plasma Burner.
The Agilent model 355 SCD provides high sensitivity (<0.5 pg S/sec), with
linear and equimolar response over four orders of magnitude (per Sulfur
atom) while maintaining high selectivity over common solvents. The Agilent
SCD is compatible with most commercially available gas chromatographs.
Nitrogen Chemiluminescence Detector
Operation of the Agilent model 255 Nitrogen Chemiluminescence Detector is
based on the chemiluminescence or light-producing reaction of ozone with
nitric oxide formed from combustion. Reacting nitric oxide with ozone results
in the formation of electronically excited nitrogen dioxide. The excited
nitrogen dioxide emits light, a chemiluminescence reaction, in the red and
infrared region of the spectrum. The light emitted is directly proportionally to
the amount of nitrogen in the sample,
NO + O
3
NO
2
NO
2
+ hη (>800 nm)
The light (hη) emitted by the chemical reaction is optically filtered and
detected by a photomultiplier tube. The signal from the photomultiplier tube is
amplified for display or output to a data system. Organic compounds
containing nitrogen react to form nitric oxide, carbon dioxide, and water.
R-N + O
2
→ NO + CO
2
+ H
2
O
H
2
/O
2
Δ
--------------
-