SYNCHRONIZATION OF DIGITAL FACILITIES B-9
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
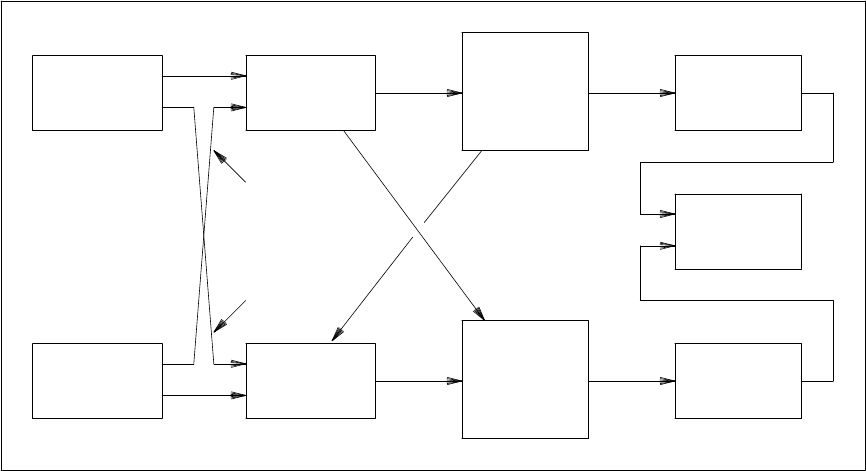
System 85 or Generic 2 with a duplicated architecture and cross-coupled cables.
MODULE
CLOCK
OR TMS
CLOCK 1
SWITCHING
NETWORK
1
PORT
CARRIERS
SWITCHING
NETWORK
0
MODULE
CLOCK
OR TMS
CLOCK 0
SCS 0
SCS 1
DS1
INTERFACE
DS1
INTERFACE
SECONDARY
PRIMARY
SECONDARY
PRIMARY
Figure B-5. Duplicated Synchronization Architecture and Cross Coupling
The TN767 is a DS1 circuit pack for a universal module; the ANN11 is a DS1 circuit pack for a traditional
module. The standard cable that comes with the TN767 is the H600307. It can be ordered in eight different
lengths, up to 650 feet, by ordering one of eight different group numbers (groups 1 - 8). See System 85
R2V4 to DEFINITY Communications System Generic 1.1 via ISDN PRI Access (555-037-233), DEFINITY
Communications System Generic 1.1 to 4ESS via ISDN PRI Access (555-037-234), and DEFINITY
Communications System Generic 2.1 to 4ESS via ISDN PRI Access (555-037-237), for specific cabling and
administrative information. The synchronization software consists of a series of tasks that monitor several
system status parameters and thus maintain the best synchronization source online. (The online source is
the synchronization reference currently in control. This reference can be either the primary or secondary
reference, or an on-board local oscillator.) Several levels of control are maintained. One level is controlled
by a 1-second software task that uses the system status to keep the best incoming DS1 reference clock
online. The other is controlled both by hardware and the 1-second software task to maintain a healthy SCS
on line. If a SCS can receive a suitable reference clock from a DS1, then the best combination is chosen.
The principal error conditions used to determine if a switch to a different DS1 clock reference is needed are,
in order of importance:
• Loss of signal (LOS) at the SCS circuit for more than 200 ms. A switch is made to the high-accuracy
clock (HAC) on the SCS by the SCS. A further analysis is then made to determine if the LOS is
network related or switch related. A switch to a healthy reference is done if appropriate.
• Blue alarm means that the switch cannot be used as a reference.
• Out-of-lock (OOL) condition means that the HAC is unable to lock onto the incoming clock from the
current DS1 reference. A switch to a healthy reference is done if one is available. Otherwise, a switch
to the HAC is performed.


















