Appendix E: Understanding IP and IP addressing 157
DMS-100 Family EIU User Guide TELECOM12
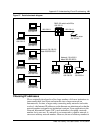
Figure 35 IP addressing: class D
Figure 36 IP addressing: class E
Address masks
For administrative or procedural reasons, a network number can be subdivided
into subnetworks using a subnetwork mask, also called a subnet or address
mask. A network mask is a set of values that masks, or causes the router to
ignore, portions of a packet address. This technique allows the administrator
to subdivide the networks at levels below the Internet address defined range.
A subnetwork mask identifies to IP the portion of the whole address that
identifies the network and subnetwork. Subnetwork masks are represented in
decimal values. For example, to indicate that the first two bytes of an address
are the network and subnetwork parts and the last two bytes are reserved for
hosts, the subnetwork mask is 255.255.0.0.
For instance, assume that IP address 133.101.0.0 has been assigned to a
company. Without a subnetwork mask, the last two fields of the address
identify individual hosts. In this case, assume the company has five major
| |
28
32
multicast
bits
bits
4 bit
Class D indicator
| ||
1110
Class D addresses are used to broadcast to all hosts on network.
Base_Tel-15
| |
28
32
experimental
bits
bits
4 bit
Class E indicator
| ||
1111
Class E addresses are experimental and are generally not used by the IP community.
Base_Tel-16