56 Chapter 2: EIU messaging protocols
297-8991-910 Standard 03.01 August 1999
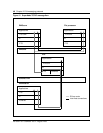
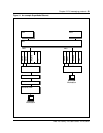
Figure 13 Typical configuration for LAN and SuperNode subnets
For more information on IP addresses, refer to “Appendix H: IP network
number requests” and “Appendix E: Understanding IP and IP addressing”.
How to get IP addresses for SuperNode
To ensure that the network portion of an IP address is unique, all IP addresses
are assigned by a central authority, the Network Information Center (NIC).
The central authority assigns the network portion of the IP address and
delegates responsibility for assigning host addresses to the requesting
organization.
It is essential for the NIC to assign IP addresses for networks that are attached
to the connected Internet. An individual organization may assign arbitrary IP
addresses without contacting NIC, but only if their network is not connected
to the public Internet. However, experience has shown that it is unwise to apply
this kind of arbitrary addressing scheme. Arbitrary schemes prevent future
interoperability and may cause significant problems and down time when
converting to NIC-assigned addresses in future. It is strongly recommended
that the operating company obtain official Internet addresses from the NIC.
What is the SuperNode network topology?
The network consists of a SuperNode switch and other third-party equipment
such as HUBs and workstations. Third party routers may be required for
distant LANs or for fault tolerant network architecture. Based on network
topology, following information may be required:
EIU
EIU
LAN-side subnet
SuperNode-side subnet
CM