— 143 —
4.1.3 Mapping of Print Data in the Print Area
Print data is mapped in the print area as follows:
(1) The print area is set by ESC W. When the printer has finished all of the print and paper feed actions
specified before receiving an ESC W, the ESC W sets the right end (as viewed facing the printer) as the
start point (x0, y0) of the print area. The print area is a rectangle defined by two edges extending from
the start point (x0, y0): one edge running in the “x” (Horizontal) direction by “dx” pitch (inclusive of the
start point), and the other running in the “y” (Vertical) direction by “dy” pitch. (If no ESC W is defined,
the default values are used to define the print area.)
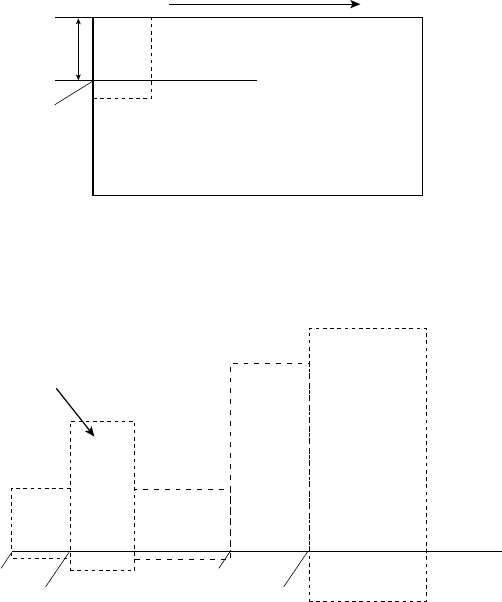
(2) With a print area defined by ESC W and a print direction specified by ESC T, when the printer receives
print data, the print data is mapped in the print area where point A (see the Figure 4-1 “Mapping Position
for Character Data”) is used as the initial value of the start point. If the print data consists of characters,
this start point serves as the baseline.
If the print data is a downloaded bitmap image or a bar code, the print data is mapped with its lower-left
point B aligned to the baseline. (See the Figure 4-2 “Mapping Positions for Print Data”.)
When attempting to map the HRI characters of a bar code, however, the section above the standard
character height will not be printed.
(3) If print data (or the space to the right of a character) extends beyond the print area before a command
that involves a line feed (for example, LF or ESC J command) is received, a line feed is automatically
executed in the print area, so that the mapping position of the print data is moved one line. The next
mapping position will be the beginning of the line. In this case, the line feed width is as defined by a
command such as ESC 2 or ESC 3.
(4) By default, the line feed width is 1/6 inch, which is equivalent to 34 dots. If the print data for the next line
includes a vertically doubled or taller character, a downloaded bitmap image extending two or more
lines, or a bar code taller than the character height, the data, therefore, falls short of the line feed width,
causing the upper dots of the character to overlap the print data of the current line. The line feed width
needs to be increased.
Figure 4-1 Mapping Position for Character Data
Figure 4-2 Mapping Positions for Print Data
A
Baseline
Point A
Print area
Mapping direction
24-3
dx, dy
x0, y0
3
A
Baseline
Point B
Point B
Double height character
Downloaded
bit image
(HRI Characters)
Bar code
GS k m
24-3
24
6*8=48
GShn
24*2-6=42
3
6
Point B
Bit image
Esc * m nL nH
12
12
x*8
Point B
nH*256+nL
GS * x y


















