16 Chapter 2
Subsystem Architecture and Components
2.2.4 Multiple Data and Control Paths
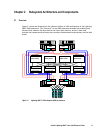
The 9900 subsystem uses a state-of-the-art architecture called the Hierarchical Star (HiStar)
Network (HSN) which utilizes multiple point-to-point data and command paths in order to
provide redundancy and improve performance. Each data and command path is independent.
The individual paths between the channel or disk adapters and cache are steered by high-
speed cache switch cards. The 9900 does not have any common buses, thus eliminating the
performance degradation and contention that can occur in a bus architecture. All data
stored on the 9900 subsystem is moved into and out of cache via the redundant high-speed
paths.
2.2.5 Redundant Power Supplies
Each storage cluster is powered by its own set of redundant power supplies, and each power
supply is able to provide power for the entire subsystem, if necessary. Because of this
redundancy, the 9900 subsystem can sustain the loss of multiple power supplies and still
continue operation. To make use of this capability, the 9900 should be connected either to
dual power sources or to different power panels, so if there is a failure on one of the power
sources, the 9900 can continue full operations using power from the alternate source.
2.2.6 Client-Host Interface Processors (CHIPs) and Channels
The CHIPs contain the front-end microprocessors which process the channel commands from
the host(s) and manage host access to cache. In the S/390
®
environment, the CHIPs perform
CKD-to-FBA and FBA-to-CKD conversion for the data in cache. The CHIPs are available in
pairs. Depending on the configuration, each CHIP in a pair contains either two or four
microprocessors and four buffers which allow data to be transferred between the CHIP and
cache. Each CHIP pair is composed of the same type of channel interface (FICON™, ExSA™, or
fibre-channel). Each ExSA™ or fibre-channel CHIP pair supports either four or eight
simultaneous data transfers to and from cache and four or eight physical connections to the
host. Each FICON™ CHIP pair supports four physical connections to the host. The 9900 can be
configured with multiple CHIP pairs to support various interface configurations. Table 2.1
lists the CHIP specifications and configurations and the number of channel connections for
each configuration.
Note: The Hitachi CruiseControl and Graph-Track products (see section 3.7) allow users to
collect and view usage statistics for the CHIPs in the 9900 subsystem.