104 Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator’s Guide
53-1002116-01
Scheduling
10
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
switch(config)#qos rcv-queue multicast rate-limit 10000
switch(config)#end
3. Enter the copy command to save the running-config file to the startup-config file.
switch#copy running-config startup-config
Scheduling
Scheduling arbitrates among multiple queues waiting to transmit a frame. The Dell M8428-k
supports both Strict Priority (SP) and Deficit Weighted Round Robin (DWRR) scheduling algorithms.
Also supported is the flexible selection of the number of traffic classes using SP-to-DWRR. When
there are multiple queues for the same traffic class, then scheduling takes these equal priority
queues into consideration.
Strict priority scheduling
Strict priority scheduling is used to facilitate support for latency-sensitive traffic. A strict priority
scheduler drains all frames queued in the highest priority queue before continuing on to service
lower priority traffic classes. A danger with this type of service is that a queue can potentially starve
out lower priority traffic classes.
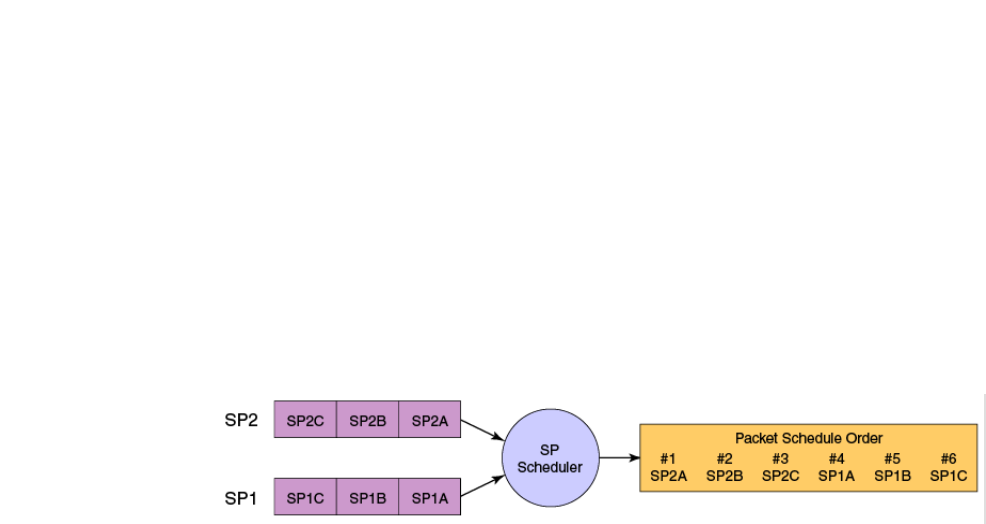
Figure 7 describes the frame scheduling order for an SP scheduler servicing two SP queues. The
higher numbered queue, SP2, has a higher priority.
FIGURE 7 Strict priority schedule — two queues
Deficit weighted round robin scheduling
Weighted Round Robin (WRR) scheduling is used to facilitate controlled sharing of the network
bandwidth. WRR assigns a weight to each queue; that value is then used to determine the amount
of bandwidth allocated to the queue. The round robin aspect of the scheduling allows each queue
to be serviced in a set ordering, sending a limited amount of data before moving onto the next
queue and cycling back to the highest priority queue after the lowest priority is serviced.


















