C141-E134-01EN 7 - 1
CHAPTER 7 ERROR ANALYSIS
7.1 Error Analysis Information Collection
7.2 Sense Data Analysis
This chapter explains in detail how sense data collected from a disk drive is used for troubleshooting. Sense
data reflects an error in the disk drive, and helps with troubleshooting.
A sense key, sense code, and subsense code, taken from various sense data are repeated. Also in this
chapter, troubleshooting is performed using these three codes. Unless otherwise specified, "sense data"
means the above three codes. When sense data is represented as (x-xx-xx), the leftmost x is a sense key, the
middle xx is a sense code, and the rightmost x is a subsense code.
7.1 Error Analysis Information Collection
7.1.1 Sense data
When IDD posts a CHECK CONDITION status or detects a fatal error in the SCSI bus, the current
command or queued command is cleared. In such a case, the IDD generates sense data about the
command-issuing INIT. The INIT can read the sense data by issuing a REQUEST SENSE
command.
Even if a transfer byte length that is shorter than the sense data length of the tested device is
specified, the command terminates normally. In this case, however, the INIT receives part of the
sense data, but the remaining part of the sense data is lost.
For details of the REQUEST SENSE command, refer to the SCSI Logical Interface Specifications.
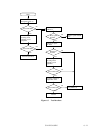
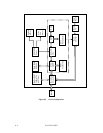
7.1.2 Sense key, sense code, and subsense code
If an error is detected in a disk drive, the error status is indicated in the sense data collected from
the disk drive. Figure 7.1 shows the positions of a sense key, sense code, and subsense code.