60
CHAPTER 3
Intel Express 10/100 Fast Ethernet Switch
Spanning Tree Commands
Spanning tree automatically configures a loop-free topology in a
bridged environment. The spanning tree agent is implemented in
conformance with the IEEE 802.1d standard. In most cases, the
defaults work fine and you won’t need to change any parameters.
Example
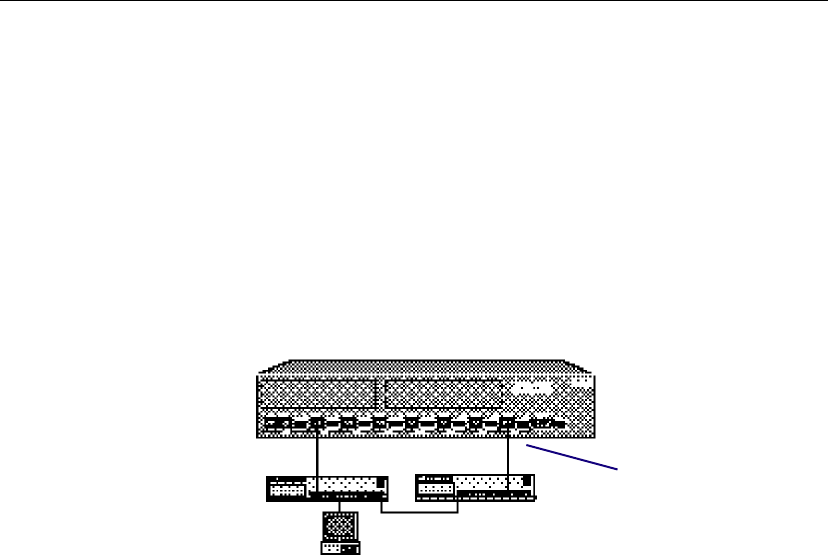
Spanning tree is enabled anytime a packet could potentially be caught
in an infinite loop on the network.
The protocol uses the port with the most efficient path and turns off
the other port. In the example, each hub is connected to switch and to
each other. Consequently, the workstation has two paths to the switch.
In Ethernet, this isn’t allowed and one of the switch ports must be
turned off. Spanning tree sends out configuration messages and
automatically determines which port is turned off. However, by
changing spanning tree parameters, you can manually determine
which port is turned off.
Spanning tree determines which port is turned off by selecting the
port with the lowest cost path. This port is then called the root bridge
(in this case, the root bridge is a switch port). Think of the lowest cost
path as the quickest route from the workstation to the switch. In the
case of a tie, the lowest numbered switch port is the root bridge. In the
example, port 2 is root bridge and port 8 is turned off.
Spanning tree disables
this port to prevent a
redundant loop.


















