5
Hardware Installation and Network Topology
CHAPTER 1
Using the Switch
The switch requires minimal user intervention. It automatically learns
the addresses of new devices as you connect them, and will relearn
addresses dynamically if you reconfigure the network. It also
automatically detects the speed of connected devices. You don’t need
to manually set the speed.
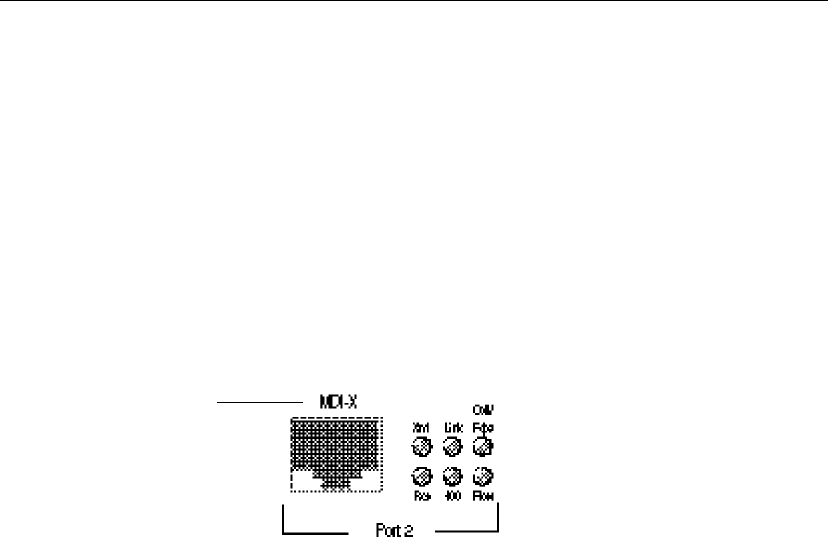
Port status LEDs
Port LEDs provide information about each port’s configuration and
the status of devices connected to the ports.
Xmt Transmit. Lights when the switch is transmitting
packets from this port to another port. Normally
blinks at regular intervals, even if no devices are
connected, while it updates the internal SNMP
agent.
Rcv Receive. Lights when packets are received on this
port, even if they are not forwarded.
Coll/Fdpx Collision (default) or Full Duplex. Blinks when
collisions are detected. Collisions are normal in an
Ethernet environment. However, if the collision
LED is on continuously, you may have a problem
with a device on the segment.
If you’ve enabled full duplex on the port, the LED is
on solid. When full duplex is enabled, collisions
aren’t possible because packets are sent and
received on their own wire pair, so they can’t
collide.
Ports on the switch are wired
MDI-X for connection to MDI
ports using a straight-through
UTP cable. See page 8 for
more information.
NOTE
The default configuration of
all ports is half-duplex mode.
To change to full duplex, use
the Console Manager. See
page 22 for instructions.


















