Geographic Mirroring Measurements
NOTE: The information that follows is based on performance measurements and analysis done in the
IBM Server Group Division laboratory. Actual performance may vary significantly from this test.
Synchronization on an idle system:
The following data shows the time required to synchronize 1 terabyte of data. This test case could vary
greatly depending on the speed and latency of communication between the two systems. In the following
measurements, the same switch was used for both the source and target systems. Also, large objects were
synchronized were synchronized, which tend to synchronize faster than small objects.
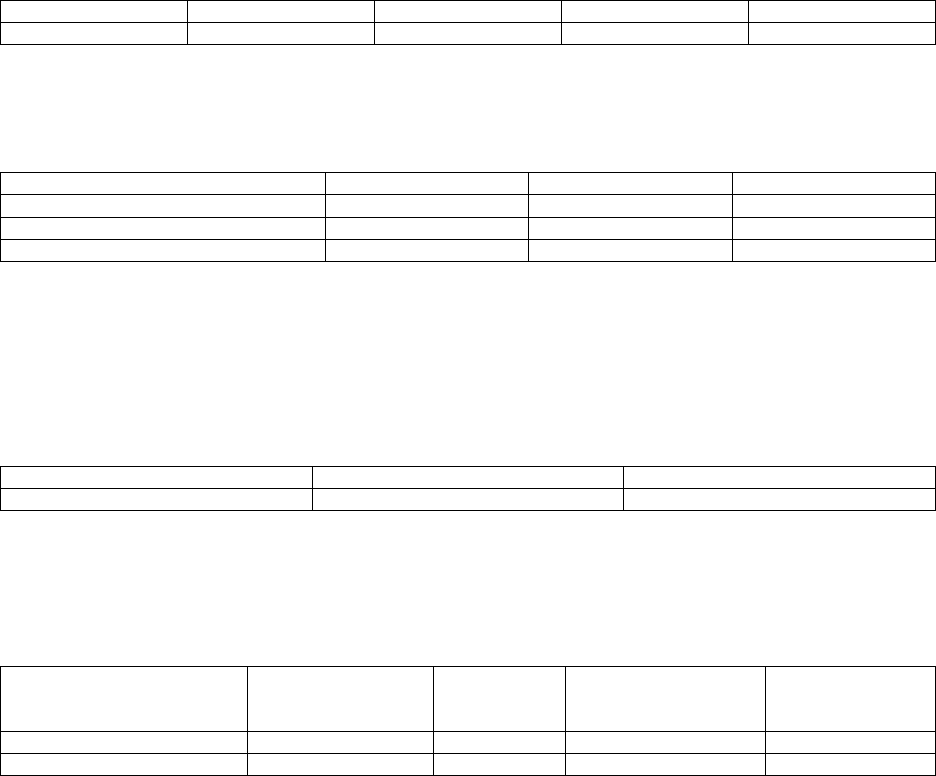
Time Required in Hours to Synchronize 1 Terabyte of Data using High Priority in Asynchronous mode
1.11.251.42.75Time(Hours)
4 Gigabit Lines3 Gigabit Lines2 Gigabit Lines1 Gigabit Line
*This case represents best case scenario. An environment with objects ¼ the size of the objects used in
this test caused synchronization times 4x’s larger.
Effects of Resume Priority Settings on Synchronization of 1 Terabyte of data using 4 gigabit lines in
Asynchronous Mode.
18%16%12%Target System CPU Overhead
16%12%9%Source System CPU Overhead
63:00 75:00 96:00Time(Minutes)
HighMediumLow
*This case represents best case scenario. An enviroment with objects ¼ the size of the objects used in this
test caused synchronization times 4x’s larger.
Switchable Towers using Geographic Mirroring:
The following data shows the time required to switch a geographic mirrored IASP that is synchronized
from the source system to the target system.
Time Required to Switch Towers using Geographic Mirroring using Asynchronous Mode
6:006:00Time(Minutes)
Active SwitchoversInactive Switchovers
Active State:
The following measurements show the CPU overhead from an System/User ASP baseline on the source
system.
CPU Overhead caused by Geographic Mirroring
13%13%13%13%Target System CPU Overhead
24%19%24%19%Source System CPU Overhead
Synchronous
Geographic
Mirroring
Synchronous
Geographic Mirroring
Synchronization Stage
Asynchronous
Geographic
Mirroring
Asynchronous
Geographic Mirroring
Synchronization Stage
• Geographic Mirroring Synchronization Stage: The number reflects the amount of CPU utilized
while in the synchronization mode on a 1-line system.
• Asynchronous Geographic Mirroring: The number reflects the overhead caused by mirroring in
asynchronous mode using 1-line system and running the CPW workload.
• Synchronous Geographic Mirroring: The number reflects overhead caused by mirroring in
synchronous mode using 1-line and running the CPW workload
IBM i 6.1 Performance Capabilities Reference - January/April/October 2008
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2008 Chapter 21 High Availability Performance 331
