• FTS is a less efficient way to transfer data. However, it offers built in data compression for line
speeds less than a given threshold. In some configurations, it will compress data when using LAN;
this significantly slows down LAN transfers.
5.8 HPR and Enterprise extender considerations
Enterprise Extender is a protocol that allows the transmission of APPC data over IP only infrastructure. In
System i support for Enterprise Extender is added in 5.4. The communications using Enterprise Extender
protocol can be achieved by creating a special kind of APPC controller, with LINKTYPE parameter of
*HPRIP.
Enterprise Extender (*HPRIP) APPC controllers are not attached to a specific line. Because of this, the
controller uses the LDLCLNKSPD parameter to determine the initial link speed to the remote system.
After a connection has been started, this speed is adjusted automatically, using the measured network
values. However if the value of LDLCLNKSPD is too different to the real link speed value at the
beginning, the initial connections will not be using optimally the network. A high value will cause too
many packets to be dropped, and a low value will cause the system not to reach the real link speed for
short bursts of data.
In a laboratory controlled environment with an isolated 100 Mbps Ethernet network, the following
average response times were observed on the system (not including the time required to start a SNA
session and allocate a conversation):
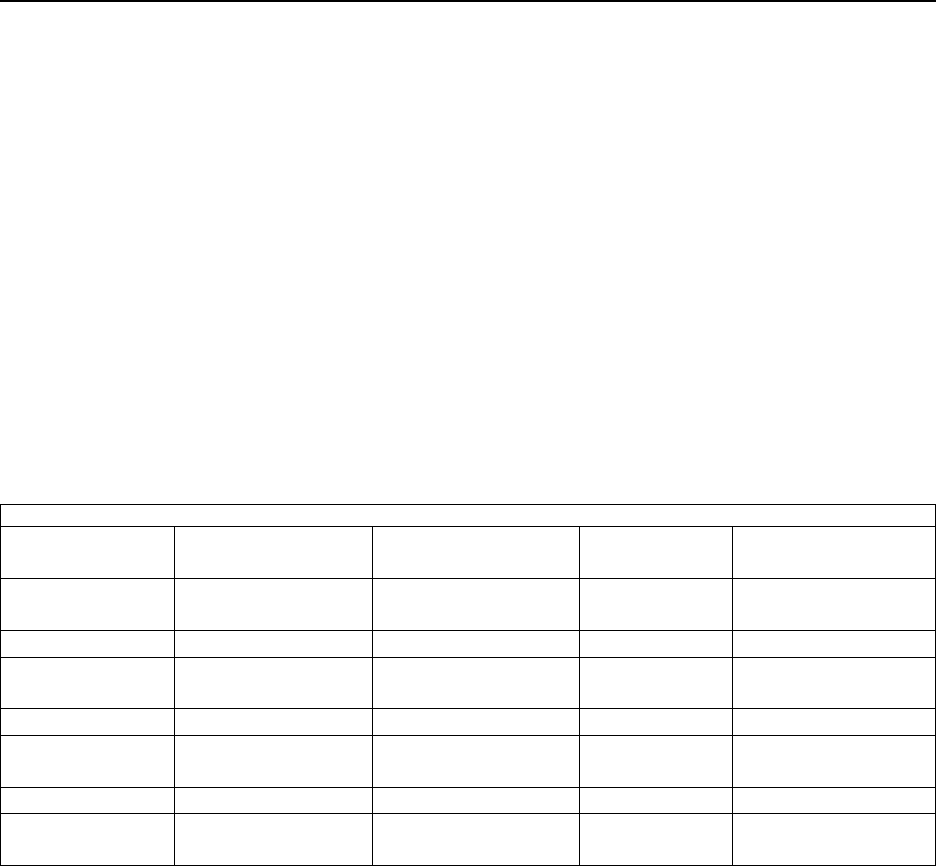
5:23 min5:40 min5:16 min5:12 minSend File using
sndnetf (1GB)
3:00 min3:33 min2:17 min2:32 min1GB Request
6:04 min7:22 min6:08 min6:14 min1GB Request
with echo
1 sec5 sec0.010 sec0.019 sec64K Request
2 sec13 sec0.010 sec0.019 sec64K Request
with echo
0.003 sec0.003 sec0.001 sec0.001 secShort Request
0.001 sec0.001 sec0.001 sec0.001 secShort Request
with echo
LANAnyNetHPRIP Link Speed
= 100Mbps
HPRIP Link
Speed = 10Mbps
Test Type
Table 5.9
The tests were done between two IBM System i5 (9406-820 and 9402-400) servers in an isolated
network.
Allocation time refers to the time that it takes for the system to start a conversation to the remote system.
The allocation time might be greater when a SNA session has not yet started to the remote system.
Measured allocation speed times where of 14 ms, in HPRIP systems in average, while in AnyNet
allocation times where of 41 ms in average.
The HPRIP controllers have slightly higher CPU usage than controllers that use a direct LAN attach. The
CPU usage is similar to the one measured on AnyNet APPC controllers. On laboratory testing, a LAN
transaction took 3 CPW, while HPRIP and AnyNet, both took 3.7 CPW.
IBM i 6.1 Performance Capabilities Reference - January/April/October 2008
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2008 Chapter 5 - Communications Performance 76
