Functional Architecture Intel
®
Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
12
Independent channel mode or lockstep mode
Data burst length of eight cycles for all memory organization modes
Memory DDR3 data transfer rates of 800, 1066, 1333, and 1600 MT/s
64-bit wide channels plus 8-bits of ECC support for each channel
DDR3 standard I/O Voltage of 1.5 V and DDR3 Low Voltage of 1.35 V
1-Gb, 2-Gb, and 4-Gb DDR3 DRAM technologies supported for these devices:
o UDIMM DDR3 – SR x8 and x16 data widths, DR – x8 data width
o RDIMM DDR3 – SR,DR, and QR – x4 and x8 data widths
o LRDIMM DDR3 – QR – x4 and x8 data widths with direct map or with rank
multiplication
Up to eight ranks supported per memory channel, 1, 2 or 4 ranks per DIMM
Open with adaptive idle page close timer or closed page policy
Per channel memory test and initialization engine can initialize DRAM to all logical zeros
with valid ECC (with or without data scrambler) or a predefined test pattern
Isochronous access support for Quality of Service (QoS)
Minimum memory configuration: independent channel support with 1 DIMM populated
Integrated dual SMBus* master controllers
Command launch modes of 1n/2n
RAS Support:
o Rank Level Sparing and Device Tagging
o Demand and Patrol Scrubbing
o DRAM Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) for any single x4 or x8 DRAM
device. Independent channel mode supports x4 SDDC. x8 SDDC requires
lockstep mode
o Lockstep mode where channels 0 and 1 and channels 2 and 3 are operated in
lockstep mode
o Data scrambling with address to ease detection of write errors to an incorrect
address.
o Error reporting through Machine Check Architecture
o Read Retry during CRC error handling checks by iMC
o Channel mirroring within a socket
CPU1 Channel Mirror Pairs (A,B) and (C,D)
CPU2 Channel Mirror Pairs (E,F) and (G,H)
o Error Containment Recovery
Improved Thermal Throttling with dynamic Closed Loop Thermal Throttling (CLTT)
Memory thermal monitoring support for DIMM temperature
3.4.1.1 Intel
®
Compute Module MFS2600KI Supported Memory
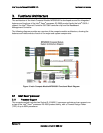
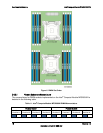
Each processor provides four banks of memory, each capable of supporting up to two DIMMs.
DIMMs are organized into physical slots on DDR3 memory channels that belong to
processor sockets.
The memory channels from processor socket 1 are identified as Channel A, B, C, and D.
The memory channels from processor socket 2 are identified as Channel E, F, G, and H.