Chapter 2---System Description
2.3.7 Raster Timing Generator PCB
The Raster Timing Generator (RTG) is located in the electronic
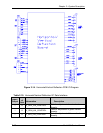
card cage (Figure 5-1). The RTG I/O diagram (Figure 2-13) and
the list of inputs and outputs (Tables 2-10 and 2-11) provide
information to allow the technician to perform module level
troubleshooting.
The following functions are provided by RTG board:
• Internal sync generation
• Sync detection and selection
• Serration and equalization pulse removal
• Phase locked loop
• Blanking pulse generation
• Horizontal and vertical phase adjustments
• Interlace detection and odd field pulse generation
• Horizontal frequency band selection
• Horizontal line count and vertical count generation
• IIC interface
• Video clamp pulse generation
• Source change detection
• HVPS sync generation
• Horizontal deflection enable circuitry
The RTG I/O Diagram (Figure 2-13) and the list of inputs and
outputs (Tables 2-7 and 2-8) provide information for the technician
to perform module level troubleshooting.
Horizontal frequency band selection and LED logic.
The RTG produces a voltage that is proportional to the horizontal
frequency which is used by the Horiz/Vert Deflection board,
System Controller Board, and the phase locked loop (PLL) section
of the RTG board. This DC voltage is used to create the following
frequency bands:
Band A: from 15 KHZ to 24.5 KHZ.
Band B: from 24 KHZ to 29.5 KHZ
Band C: from 29 KHZ to 56 KHZ
Band D: from 55.5 KHZ to 90 KHZ.
These bands are outputted through the IIC interface to be used
by the System Controller Board. These lines are also outputs of
the RTG board through the Backplane Board. The
2-40 Model 200 Service Manual