7FH
2FH
2EH
2DH
2CH
2BH
2AH
29H
28H
27H
26H
25H
24H
23H
22H
21H
20H
1FH
18H
17H
10H
0FH
08H
07H
00H
BANK 3
BANK 2
BANK 1
BANK 0
MSB LSB
7F 7E 7D 7C 7B 7A 79 78
77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70
6F 6E 6D 6C 6B 6A 69 68
67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60
5F 5E 5D 5C 5B 5A 59 58
57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50
4F 4E 4D 4C 4B 4A 49 48
47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40
3F 3E 3D 3C 3B 3A 39 38
37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30
2F 2E 2D 2C 2B 2A 28 28
27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20
1F 1E 1D 1C 1B 1A 19 18
17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10
0F 0E 0D 0C 0B 0A 09 08
07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
USER’S GUIDE
050396 11/173
12
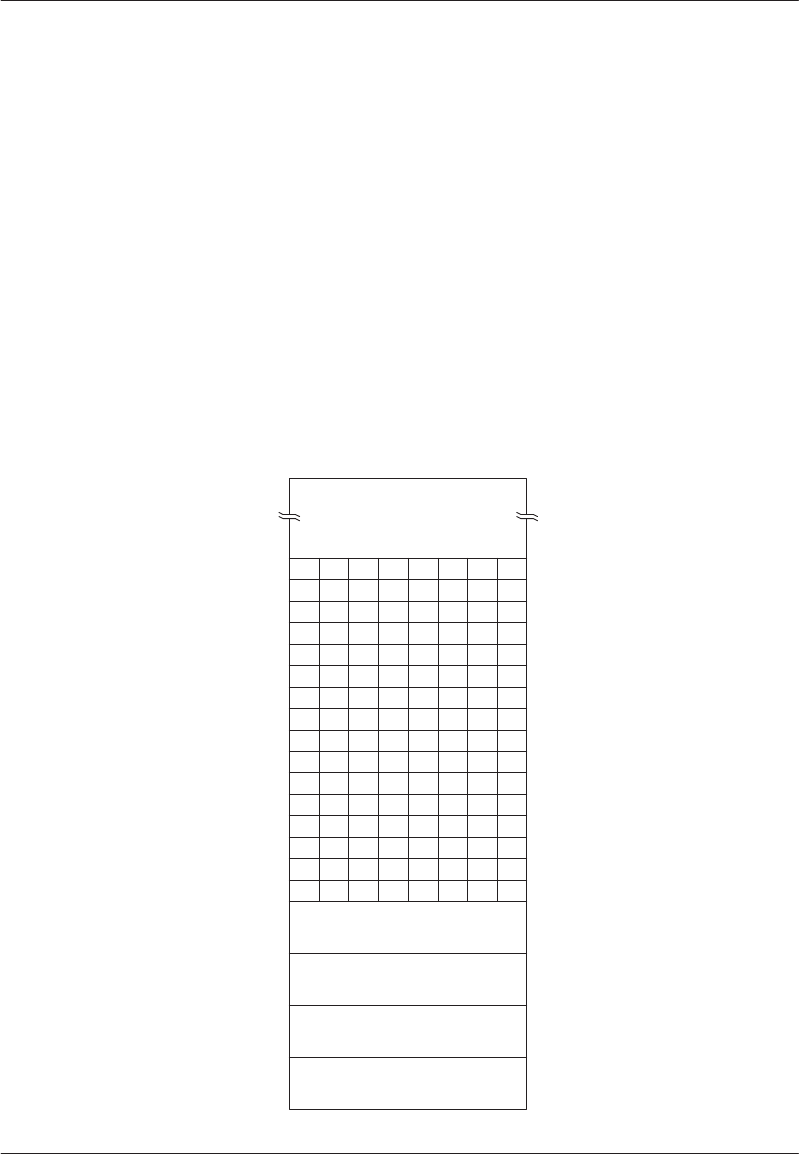
The Scratchpad Registers are general purpose data
storage RAM. They are commonly used for temporary
storage of a small number of variables when high–
speed access is needed. Off–chip RAM (MOVX) is
used when the quantity of data is larger than 128 bytes.
The Scratchpad Registers are lithium backed and will
be preserved in the absence of power.
The Scratchpad area has two additional functions. First,
16 bytes of the Scratchpad area are bit addressable.
That is, while each byte has an address of its own, these
bits also have individual bit addresses. Certain instruc-
tions operate on bits instead of bytes. Although the ad-
dresses appear the same, the microprocessor can dis-
tinguish a bit address from a byte address by the
instruction used. A large number of individual software
flags and conditions can be represented using 128
(16*8) individually addressable bits.
A second use of the Scratchpad area is for the program-
mer’s stack. Like the 8051, the Secure Microcontroller
uses a Stack Pointer (SP – 81h) SFR to direct stack ac-
cess into the internal registers. The SP has a default val-
ue of 07h. This means that stack storage will begin at
location 08h. Each PUSH or CALL instruction will incre-
ment the SP. Note that while the SP is located in the SFR
area, the stack itself is stored in the Scratchpad area.
The Scratchpad Register Memory map is shown in
Figure 4–2.
Programmer’s note
: with the use of ‘C’ com-
pilers becoming more frequent, the large memory mod-
el should be examined. This compiler model places the
stack in off–chip SRAM. Secure Microcontroller based
systems usually have an abundance of such SRAM
compared to ROM based systems. While off–chip stack
results in slower execution time, the stack size becomes
virtually unlimited.
SCRATCHPAD REGISTER MAP Figure 4–2


















